Caspase-11-mediated endothelial pyroptosis underlies endotoxemia-induced lung injury
- PMID: 28990935
- PMCID: PMC5663346
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI94495
Caspase-11-mediated endothelial pyroptosis underlies endotoxemia-induced lung injury
Abstract
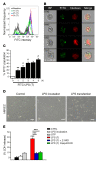
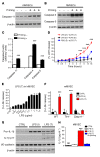
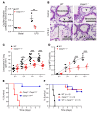
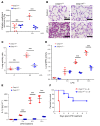
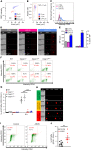
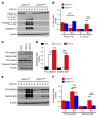
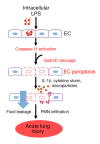
Acute lung injury is a leading cause of death in bacterial sepsis due to the wholesale destruction of the lung endothelial barrier, which results in protein-rich lung edema, influx of proinflammatory leukocytes, and intractable hypoxemia. Pyroptosis is a form of programmed lytic cell death that is triggered by inflammatory caspases, but little is known about its role in EC death and acute lung injury. Here, we show that systemic exposure to the bacterial endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS) causes severe endothelial pyroptosis that is mediated by the inflammatory caspases, human caspases 4/5 in human ECs, or the murine homolog caspase-11 in mice in vivo. In caspase-11-deficient mice, BM transplantation with WT hematopoietic cells did not abrogate endotoxemia-induced acute lung injury, indicating a central role for nonhematopoietic caspase-11 in endotoxemia. Additionally, conditional deletion of caspase-11 in ECs reduced endotoxemia-induced lung edema, neutrophil accumulation, and death. These results establish the requisite role of endothelial pyroptosis in endotoxemic tissue injury and suggest that endothelial inflammatory caspases are an important therapeutic target for acute lung injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

