Impact of Mother-Daughter Relationship on Hypertension Self-management and Quality of Life: Testing Dyadic Dynamics Using the Actor-Partner Interdependence Model
- PMID: 28990970
- PMCID: PMC5886818
- DOI: 10.1097/JCN.0000000000000448
Impact of Mother-Daughter Relationship on Hypertension Self-management and Quality of Life: Testing Dyadic Dynamics Using the Actor-Partner Interdependence Model
Abstract
Background: Although hypertension (HTN) treatment rates are similar across age groups of women, effective control is significantly worse among older women. Only 20% of hypertensive women aged 70 to 79 years have controlled blood pressure.
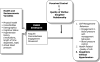
Objectives: The purpose of this longitudinal study was to test the effects of the quality of mother-daughter relationship, inner strength, and control on HTN self-management and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) for both members of the dyad at 6 months. The Actor-Partner Interdependence Model was used to examine the direct ("actor") and indirect ("partner") effects of 46 dyads.
Results: The mothers' perceived relationship quality with daughters directly impacted their own self-management of HTN and HRQOL while also indirectly affecting their daughters' self-management. Similarly, the daughters' perceived strength of their relationship with their mothers directly influenced their self-management and HRQOL and indirectly affected their mothers' self-management and HRQOL.
Figures
References
-
- Nwankwo T, Yoon SS, Burt V, Gu Q. Hypertension among adults in the United States: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2011–2012. Vol. 133. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2013. - PubMed
-
- Nwankwo T National Center for Health S. Hypertension among adults in the United States : National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2011–2012. 2013 - PubMed
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Healthy People 2020. Washington, DC: 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical