Translational Implication of Galectin-9 in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Viral Infection
- PMID: 28991189
- PMCID: PMC5666790
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18102108
Translational Implication of Galectin-9 in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Viral Infection
Abstract
The interaction between galectin-9 and its receptor, Tim-3, triggers a series of signaling events that regulate immune responses. The expression of galectin-9 has been shown to be increased in a variety of target cells of many different viruses, such as hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), herpes simplex virus (HSV), influenza virus, dengue virus (DENV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). This enhanced expression of galectin-9 following viral infection promotes significant changes in the behaviors of the virus-infected cells, and the resulting events tightly correlate with the immunopathogenesis of the viral disease. Because the human immune response to different viral infections can vary, and the lack of appropriate treatment can have potentially fatal consequences, understanding the implications of galectin-9 is crucial for developing better methods for monitoring and treating viral infections. This review seeks to address how we can apply the current understanding of galectin-9 function to better understand the pathogenesis of viral infection and better treat viral diseases.
Keywords: galectin-9; pathogenesis; translational medicine; treatment; viral infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
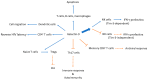
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

