Evaluating the Effects of an Organic Extract from the Mediterranean Sponge Geodia cydonium on Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 28991212
- PMCID: PMC5666794
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18102112
Evaluating the Effects of an Organic Extract from the Mediterranean Sponge Geodia cydonium on Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
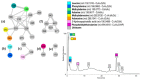
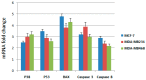
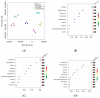
Marine sponges are an excellent source of bioactive secondary metabolites for pharmacological applications. In the present study, we evaluated the chemistry, cytotoxicity and metabolomics of an organic extract from the Mediterranean marine sponge Geodia cydonium, collected in coastal waters of the Gulf of Naples. We identified an active fraction able to block proliferation of breast cancer cell lines MCF-7, MDA-MB231, and MDA-MB468 and to induce cellular apoptosis, whereas it was inactive on normal breast cells (MCF-10A). Metabolomic studies showed that this active fraction was able to interfere with amino acid metabolism, as well as to modulate glycolysis and glycosphingolipid metabolic pathways. In addition, the evaluation of the cytokinome profile on the polar fractions of three treated breast cancer cell lines (compared to untreated cells) demonstrated that this fraction induced a slight anti-inflammatory effect. Finally, the chemical entities present in this fraction were analyzed by liquid chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry combined with molecular networking.
Keywords: breast cancer; cytokines; cytotoxicity; metabolomics; sponges.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Methanol Extract from the Marine Sponge Geodia cydonium on the Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cell Line.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:204975. doi: 10.1155/2015/204975. Epub 2015 Sep 27. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 26491222 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-proliferative and cytotoxic activities of Allium autumnale P. H. Davis (Amaryllidaceae) on human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jan 25;18(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2105-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29370794 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic Profiling Reveals the N-Acyl-Taurine Geodiataurine in Extracts from the Marine Sponge Geodia macandrewii (Bowerbank).J Nat Prod. 2016 May 27;79(5):1285-91. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00966. Epub 2016 Apr 21. J Nat Prod. 2016. PMID: 27100857
-
Effects of Galium aparine extract on the cell viability, cell cycle and cell death in breast cancer cell lines.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jun 20;186:305-310. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 Apr 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27085941
-
Identifying peach and plum polyphenols with chemopreventive potential against estrogen-independent breast cancer cells.J Agric Food Chem. 2009 Jun 24;57(12):5219-26. doi: 10.1021/jf900259m. J Agric Food Chem. 2009. PMID: 19530711
Cited by
-
Oceans as a Source of Immunotherapy.Mar Drugs. 2019 May 10;17(5):282. doi: 10.3390/md17050282. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31083446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Chemical Diversity of Phorbas Sponges as a Source of Novel Lead Compounds in Drug Discovery.Mar Drugs. 2021 Nov 26;19(12):667. doi: 10.3390/md19120667. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34940666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organic extract of Geodia cydonium induces cell cycle block in human mesothelioma cells.Oncol Lett. 2022 Jun 28;24(2):286. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13406. eCollection 2022 Aug. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35814825 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling feeding activity, growth rates and molecular data shows dietetic needs of Ciona robusta (Ascidiacea, Phlebobranchia) in automatic culture plants.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 9;10(1):11295. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68031-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32647309 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Demospongiae: A Challenging Treasure of Bioactive Compounds.Mar Drugs. 2022 Mar 31;20(4):244. doi: 10.3390/md20040244. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35447918 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sarà M., Vacelet J. Ècologie des Demosponges. In: Grassè P.P., editor. Traitè de Zoologie: Spongiaires. Volume 3. Masson et Cie; Paris, France: 1973. pp. 462–576.
-
- Hooper J.N.A., van Soest R.W.M. Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges. Kluwer Plenum; New York, NY, USA: 2002. pp. 71–82.
-
- Mayer A.M., Rodriguez A.D., Taglialatela-Scafati O., Fusetani N. Marine pharmacology in 2009–2011: Marine compounds with antibacterial, antidiabetic, antifungal, antinflammatory, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities, affecting the immune and nervous system, and others miscellanous mechanism of action. Mar. Drugs. 2013;11:2510–2573. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

