Polypharmacology-based ceritinib repurposing using integrated functional proteomics
- PMID: 28991240
- PMCID: PMC5909815
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.2489
Polypharmacology-based ceritinib repurposing using integrated functional proteomics
Abstract
Targeted drugs are effective when they directly inhibit strong disease drivers, but only a small fraction of diseases feature defined actionable drivers. Alternatively, network-based approaches can uncover new therapeutic opportunities. Applying an integrated phenotypic screening, chemical and phosphoproteomics strategy, here we describe the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) inhibitor ceritinib as having activity across several ALK-negative lung cancer cell lines and identify new targets and network-wide signaling effects. Combining pharmacological inhibitors and RNA interference revealed a polypharmacology mechanism involving the noncanonical targets IGF1R, FAK1, RSK1 and RSK2. Mutating the downstream signaling hub YB1 protected cells from ceritinib. Consistent with YB1 signaling being known to cause taxol resistance, combination of ceritinib with paclitaxel displayed strong synergy, particularly in cells expressing high FAK autophosphorylation, which we show to be prevalent in lung cancer. Together, we present a systems chemical biology platform for elucidating multikinase inhibitor polypharmacology mechanisms, subsequent design of synergistic drug combinations, and identification of mechanistic biomarker candidates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

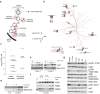
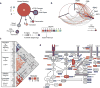
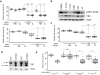
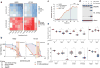
Comment in
-
Cancer systems biology: Harnessing off-target effects.Nat Chem Biol. 2017 Nov 21;13(12):1204-1205. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2519. Nat Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 29161245 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sawyers CL, et al. Imatinib induces hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in myeloid blast crisis: results of a phase II study. Blood. 2002;99:3530–3539. - PubMed
-
- Flanagan ME, et al. Discovery of CP-690,550: a potent and selective Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and organ transplant rejection. J Med Chem. 2010;53:8468–8484. - PubMed
-
- Palla G, Derényi I, Farkas I, Vicsek T. Uncovering the overlapping community structure of complex networks in nature and society. Nature. 2005;435:814–818. - PubMed
-
- Farkas IJ, et al. Network-Based Tools for the Identification of Novel Drug Targets. Sci Signal. 2011;4:pt3–pt3. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

