Structural basis for GABAA receptor potentiation by neurosteroids
- PMID: 28991263
- PMCID: PMC6166781
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.3484
Structural basis for GABAA receptor potentiation by neurosteroids
Abstract
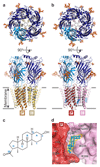
Type A γ-aminobutyric acid receptors (GABAARs) are the principal mediators of inhibitory neurotransmission in the human brain. Endogenous neurosteroids interact with GABAARs to regulate acute and chronic anxiety and are potent sedative, analgesic, anticonvulsant and anesthetic agents. Their mode of binding and mechanism of receptor potentiation, however, remain unknown. Here we report crystal structures of a chimeric GABAAR construct in apo and pregnanolone-bound states. The neurosteroid-binding site is mechanically coupled to the helices lining the ion channel pore and modulates the desensitization-gate conformation. We demonstrate that the equivalent site is responsible for physiological, heteromeric GABAAR potentiation and explain the contrasting modulatory properties of 3a versus 3b neurosteroid epimers. These results illustrate how peripheral lipid ligands can regulate the desensitization gate of GABAARs, a process of broad relevance to pentameric ligand-gated ion channels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


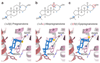


References
-
- Nemecz A, Prevost MS, Menny A, Corringer PJ. Emerging Molecular Mechanisms of Signal Transduction in Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channels. Neuron. 2016;90:452–70. - PubMed
-
- Miller PS, Smart TG. Binding, activation and modulation of Cys-loop receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2010;31:161–74. - PubMed
-
- Hosie AM, Wilkins ME, da Silva HM, Smart TG. Endogenous neurosteroids regulate GABAA receptors through two discrete transmembrane sites. Nature. 2006;444:486–9. - PubMed
-
- Majewska MD, Harrison NL, Schwartz RD, Barker JL, Paul SM. Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science. 1986;232:1004–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

