A structural model for microtubule minus-end recognition and protection by CAMSAP proteins
- PMID: 28991265
- PMCID: PMC6134180
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.3483
A structural model for microtubule minus-end recognition and protection by CAMSAP proteins
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: A structural model for microtubule minus-end recognition and protection by CAMSAP proteins.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2020 Jun;27(6):603. doi: 10.1038/s41594-020-0382-z. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32355336
Abstract
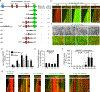
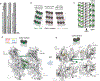
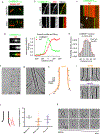
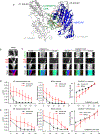
CAMSAP and Patronin family members regulate microtubule minus-end stability and localization and thus organize noncentrosomal microtubule networks, which are essential for cell division, polarization and differentiation. Here, we found that the CAMSAP C-terminal CKK domain is widely present among eukaryotes and autonomously recognizes microtubule minus ends. Through a combination of structural approaches, we uncovered how mammalian CKK binds between two tubulin dimers at the interprotofilament interface on the outer microtubule surface. In vitro reconstitution assays combined with high-resolution fluorescence microscopy and cryo-electron tomography suggested that CKK preferentially associates with the transition zone between curved protofilaments and the regular microtubule lattice. We propose that minus-end-specific features of the interprotofilament interface at this site serve as the basis for CKK's minus-end preference. The steric clash between microtubule-bound CKK and kinesin motors explains how CKK protects microtubule minus ends against kinesin-13-induced depolymerization and thus controls the stability of free microtubule minus ends.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Howard J & Hyman AA Dynamics and mechanics of the microtubule plus end. Nature 422, 753–758. (2003). - PubMed
-
- Akhmanova A & Steinmetz MO Control of microtubule organization and dynamics: two ends in the limelight. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16, 711–726 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Dammermann A, Desai A & Oegema K The minus end in sight. Curr Biol 13, R614–624 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Akhmanova A & Hoogenraad CC Microtubule minus-end-targeting proteins. Curr Biol 25, R162–171 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

