Cytotoxic and regulatory roles of mucosal-associated invariant T cells in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 28991267
- PMCID: PMC6025738
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.3854
Cytotoxic and regulatory roles of mucosal-associated invariant T cells in type 1 diabetes
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Cytotoxic and regulatory roles of mucosal-associated invariant T cells in type 1 diabetes.Nat Immunol. 2018 Sep;19(9):1035. doi: 10.1038/s41590-017-0023-9. Nat Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29880894
Abstract
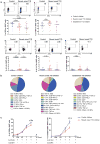
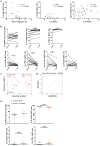
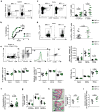
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease that results from the destruction of pancreatic β-cells by the immune system that involves innate and adaptive immune cells. Mucosal-associated invariant T cells (MAIT cells) are innate-like T-cells that recognize derivatives of precursors of bacterial riboflavin presented by the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-related molecule MR1. Since T1D is associated with modification of the gut microbiota, we investigated MAIT cells in this pathology. In patients with T1D and mice of the non-obese diabetic (NOD) strain, we detected alterations in MAIT cells, including increased production of granzyme B, which occurred before the onset of diabetes. Analysis of NOD mice that were deficient in MR1, and therefore lacked MAIT cells, revealed a loss of gut integrity and increased anti-islet responses associated with exacerbated diabetes. Together our data highlight the role of MAIT cells in the maintenance of gut integrity and the control of anti-islet autoimmune responses. Monitoring of MAIT cells might represent a new biomarker of T1D, while manipulation of these cells might open new therapeutic strategies.
Figures
Comment in
-
MAIT cells in type 1 diabetes: a good friend turned bad.Nat Immunol. 2017 Nov 16;18(12):1283-1285. doi: 10.1038/ni.3869. Nat Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29144503 No abstract available.
-
MAIT Cells: A Link between Gut Integrity and Type 1 Diabetes.Cell Metab. 2017 Dec 5;26(6):813-815. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.11.007. Cell Metab. 2017. PMID: 29211981
References
-
- Diana J, et al. Crosstalk between neutrophils, B-1a cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells initiates autoimmune diabetes. Nat Med. 2013;19:65–73. - PubMed
-
- Anderson MS, Bluestone JA. The NOD mouse: a model of immune dysregulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:447–485. - PubMed
-
- Lehuen A, Diana J, Zaccone P, Cooke A. Immune cell crosstalk in type 1 diabetes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:501–513. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials