A Platelet Factor 4-Dependent Platelet Activation Assay Facilitates Early Detection of Pathogenic Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Antibodies
- PMID: 28991552
- PMCID: PMC5812761
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.06.001
A Platelet Factor 4-Dependent Platelet Activation Assay Facilitates Early Detection of Pathogenic Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia Antibodies
Abstract
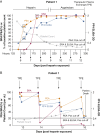
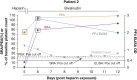
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a dangerous complication of heparin therapy. HIT diagnosis is established by recognizing thrombocytopenia and/or thrombosis in an affected patient and from the results of serological tests such as the platelet factor 4 (PF4)/heparin immunoassay (PF4 ELISA) and serotonin release assay (SRA). Recent studies suggest that HIT antibodies activate platelets by recognizing PF4 in a complex with platelet glycosaminoglycans (and/or polyphosphates) and that an assay based on this principle, the PF4-dependent P-selectin expression assay (PEA), may be even more accurate than the SRA for HIT diagnosis. Here, we demonstrate that the PEA detected pathogenic antibodies before the SRA became positive in two patients with HIT studied serially, in one case even before seropositivity in the PF4 ELISA. In one of the patients treated with plasma exchange, persistent dissociation between the PEA and SRA test results was observed. These results support a role for the PEA in early HIT diagnosis.
Keywords: HIT; early diagnosis of HIT; heparin; plasma exchange, plasmapheresis; thrombocytopenia.
Copyright © 2017 American College of Chest Physicians. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Cuker A. Management of the multiple phases of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost. 2016;116(5):835–842. - PubMed
-
- Visentin G.P., Moghaddam M., Beery S.E., McFarland J.G., Aster R.H. Heparin is not required for detection of antibodies associated with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia/thrombosis. J Lab Clin Med. 2001;138(1):22–31. - PubMed
-
- Amiral J., Bridey F., Dreyfus M. Platelet factor 4 complexed to heparin is the target for antibodies generated in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost. 1992;68(1):95–96. - PubMed
-
- Kelton J.G., Smith J.W., Warkentin T.E., Hayward C.P., Denomme G.A., Horsewood P. Immunoglobulin G from patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia binds to a complex of heparin and platelet factor 4. Blood. 1994;83(11):3232–3239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

