Diversity of cis-regulatory elements associated with auxin response in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 28992117
- PMCID: PMC5853796
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erx254
Diversity of cis-regulatory elements associated with auxin response in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
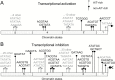
The phytohormone auxin regulates virtually every developmental process in land plants. This regulation is mediated via de-repression of DNA-binding auxin response factors (ARFs). ARFs bind TGTC-containing auxin response cis-elements (AuxREs), but there is growing evidence that additional cis-elements occur in auxin-responsive regulatory regions. The repertoire of auxin-related cis-elements and their involvement in different modes of auxin response are not yet known. Here we analyze the enrichment of nucleotide hexamers in upstream regions of auxin-responsive genes associated with auxin up- or down-regulation, with early or late response, ARF-binding domains, and with different chromatin states. Intriguingly, hexamers potentially bound by basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) and basic leucine zipper (bZIP) factors as well as a family of A/T-rich hexamers are more highly enriched in auxin-responsive regions than canonical TGTC-containing AuxREs. We classify and annotate the whole spectrum of enriched hexamers and discuss their patterns of enrichment related to different modes of auxin response.
Keywords: ARF; AuxRE; Auxin; bHLH; bZIP; bioinformatics; chromatin states; transcriptional regulation.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures



References
-
- Abel S, Nguyen MD, Theologis A. 1995. The PS-IAA4/5-like family of early auxin-inducible mRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Journal of Molecular Biology 251, 533–549. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D. 2001. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Annals of Statistics 29, 1165–1188.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

