Phenotypic Optimization of Urea-Thiophene Carboxamides To Yield Potent, Well Tolerated, and Orally Active Protective Agents against Aminoglycoside-Induced Hearing Loss
- PMID: 28992413
- PMCID: PMC5889090
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00932
Phenotypic Optimization of Urea-Thiophene Carboxamides To Yield Potent, Well Tolerated, and Orally Active Protective Agents against Aminoglycoside-Induced Hearing Loss
Abstract
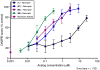
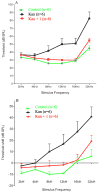
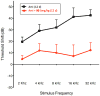
Hearing loss is a major public health concern with no pharmaceutical intervention for hearing protection or restoration. Using zebrafish neuromast hair cells, a robust model for mammalian auditory and vestibular hair cells, we identified a urea-thiophene carboxamide, 1 (ORC-001), as protective against aminoglycoside antibiotic (AGA)-induced hair cell death. The 50% protection (HC50) concentration conferred by 1 is 3.2 μM with protection against 200 μM neomycin approaching 100%. Compound 1 was sufficiently safe and drug-like to validate otoprotection in an in vivo rat hearing loss model. We explored the structure-activity relationship (SAR) of this compound series to improve otoprotective potency, improve pharmacokinetic properties and eliminate off-target activity. We present the optimization of 1 to yield 90 (ORC-13661). Compound 90 protects mechanosensory hair cells with HC50 of 120 nM and demonstrates 100% protection in the zebrafish assay and superior physiochemical, pharmacokinetic, and toxicologic properties, as well as complete in vivo protection in rats.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Part of the research reported was funded by Oricula Therapeutics. G.J., V.E.G., D.W.R., E.WR and J.A.S are founders of Oricula Therapeutics.
Figures




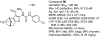

Similar articles
-
Identification of genetic and chemical modulators of zebrafish mechanosensory hair cell death.PLoS Genet. 2008 Feb 29;4(2):e1000020. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000020. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18454195 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of noise- and drug-induced hearing loss with D-methionine.Hear Res. 2007 Apr;226(1-2):92-103. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2006.11.012. Epub 2007 Jan 16. Hear Res. 2007. PMID: 17224251
-
Identification of small molecule inhibitors of cisplatin-induced hair cell death: results of a 10,000 compound screen in the zebrafish lateral line.Otol Neurotol. 2015 Mar;36(3):519-25. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000487. Otol Neurotol. 2015. PMID: 25687728 Free PMC article.
-
Drug screening for hearing loss: using the zebrafish lateral line to screen for drugs that prevent and cause hearing loss.Drug Discov Today. 2010 Apr;15(7-8):265-71. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Jan 22. Drug Discov Today. 2010. PMID: 20096805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ototoxicity.Kidney Int. 2007 Oct;72(8):931-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5002434. Epub 2007 Jul 25. Kidney Int. 2007. PMID: 17653135 Review.
Cited by
-
Flight for fish in drug discovery: a review of zebrafish-based screening of molecules.Biol Lett. 2023 Aug;19(8):20220541. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2022.0541. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37528729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbonyl 1,2-transposition through triflate-mediated α-amination.Science. 2021 Nov 5;374(6568):734-740. doi: 10.1126/science.abl7854. Epub 2021 Nov 4. Science. 2021. PMID: 34735246 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Druggable Binding Sites and Small Molecules as Modulators of TMC1.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 20:2024.03.05.583611. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.05.583611. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Commun Biol. 2025 May 13;8(1):742. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07943-x. PMID: 38826329 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A versatile, automated and high-throughput drug screening platform for zebrafish embryos.Biol Open. 2021 Sep 15;10(9):bio058513. doi: 10.1242/bio.058513. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Biol Open. 2021. PMID: 34472582 Free PMC article.
-
Visible light-initiated radical 1,3-difunctionalization of β,γ-unsaturated ketones.Sci Adv. 2022 Dec 9;8(49):eabq8596. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abq8596. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36490351 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Miscellaneous

