Inflammatory Mediators in Mood Disorders: Therapeutic Opportunities
- PMID: 28992428
- PMCID: PMC5826556
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010617-052823
Inflammatory Mediators in Mood Disorders: Therapeutic Opportunities
Abstract
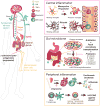
Mood disorders such as depression are among the most prevalent psychiatric disorders in the United States, but they are inadequately treated in a substantial proportion of patients. Accordingly, neuropsychiatric research has pivoted from investigation of monoaminergic mechanisms to exploration of novel mediators, including the role of inflammatory processes. Subsets of mood disorder patients exhibit immune-related abnormalities, including elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines, monocytes, and neutrophils in the peripheral circulation; dysregulation of neuroglia and blood-brain barrier function; and disruption of gut microbiota. The field of psychoneuroimmunology is one of great therapeutic opportunity, yielding experimental therapeutics for mood disorders, such as peripheral cytokine targeting antibodies, microglia and astrocyte targeting therapies, and probiotic treatments for gut dysbiosis, and producing findings that identify therapeutic targets for future development.
Keywords: inflammation; major depressive disorder; microbiome; mood disorders; therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O, Jin R, Merikangas KR, Walters EE. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Archives of general psychiatry. 2005;62:593–602. - PubMed
-
- Lopez AD, Murray CC. The global burden of disease, 1990–2020. Nat Med. 1998;4:1241–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

