The resting perfusion pattern associates with functional decline in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 28992987
- PMCID: PMC5687828
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.09.004
The resting perfusion pattern associates with functional decline in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
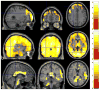
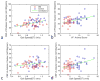
We investigated the relationships between cerebral blood flow (CBF), cognitive, and mobility decline in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) over a 2-year period. Seventy-three participants (41 T2DM and 32 controls) were evaluated using volumetric CBF with arterial spin labeling perfusion magnetic resonance imaging at baseline and at the 2-year follow-up. Regions with significant CBF differences between T2DM participants and controls at baseline were detected using voxel-wise analysis. Correlation analysis was performed to investigate the association between regional CBF and cognitive or mobility performance over the 2-year span. Compared to controls, participants with T2DM had decreased CBF in the resting-state default mode, visual, and cerebellum networks. Greater decrease in longitudinal CBF values at these regions over a 2-year span was associated with worse gait, memory and executive functions, and higher baseline insulin resistance and worse baseline cognitive performance. In T2DM, impairment of resting regional perfusion is closely related to worse cognitive and mobility performance. Insulin resistance may further contribute to regional perfusion deficit in T2DM.
Keywords: Arterial spin labeling MRI; Cerebral blood flow; Cognitive impairment; Insulin resistance; Type 2 diabetes mellitus; Voxel-based analyses.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest. Appropriate approval and procedures were used concerning human subjects.
Figures


References
-
- Alsop DC, Detre JA. Reduced transit-time sensitivity in noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging of Human cerebral blood flow. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996;16:1236–49. - PubMed
-
- Alsop DC, Detre JA, Golay X, Gunther M, Hendrikse J, Hernandez-Garcia L, Lu H, Macintosh BJ, Parkes LM, Smits M, van Osch MJ, Wang DJ, Wong EC, Zaharchuk G. Recommended implementation of arterial spin-labeled perfusion MRI for clinical applications: A consensus of the ISMRM perfusion study group and the European consortium for ASL in dementia. Magn Reson Med. 2014 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Unified segmentation. Neuroimage. 2005;26:839–51. - PubMed
-
- Benton AL, Hamsher K. Multilingual Aphasia Examination. Manual of instructions. 2. AJA Associates; Iowa City: 1989.
-
- Brownlee M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes. 2005;54:1615–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

