Characterization of novel monoclonal antibodies against the MERS-coronavirus spike protein and their application in species-independent antibody detection by competitive ELISA
- PMID: 28993122
- PMCID: PMC7113858
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2017.10.008
Characterization of novel monoclonal antibodies against the MERS-coronavirus spike protein and their application in species-independent antibody detection by competitive ELISA
Abstract
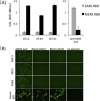
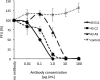
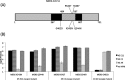
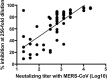
Since discovering the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) as a causative agent of severe respiratory illness in the Middle East in 2012, serological testing has been conducted to assess antibody responses in patients and to investigate the zoonotic reservoir of the virus. Although the virus neutralization test is the gold standard assay for MERS diagnosis and for investigating the zoonotic reservoir, it uses live virus and so must be performed in high containment laboratories. Competitive ELISA (cELISA), in which a labeled monoclonal antibody (MAb) competes with test serum antibodies for target epitopes, may be a suitable alternative because it detects antibodies in a species-independent manner. In this study, novel MAbs against the spike protein of MERS-CoV were produced and characterized. One of these MAbs was used to develop a cELISA. The cELISA detected MERS-CoV-specific antibodies in sera from MERS-CoV-infected rats and rabbits immunized with the spike protein of MERS-CoV. The MAb-based cELISA was validated using sera from Ethiopian dromedary camels. Relative to the neutralization test, the cELISA detected MERS-CoV-specific antibodies in 66 Ethiopian dromedary camels with a sensitivity and specificity of 98% and 100%, respectively. The cELISA and neutralization test results correlated well (Pearson's correlation coefficients=0.71-0.76, depending on the cELISA serum dilution). This cELISA may be useful for MERS epidemiological investigations on MERS-CoV infection.
Keywords: Competitive ELISA; Epidemiology; MERS coronavirus; Neutralizing antibody.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Al Hammadi Z.M., Chu D.K., Eltahir Y.M., Al Hosani F., Al Mulla M., Tarnini W., Hall A.J., Perera R.A., Abdelkhalek M.M., Peiris J.S., Al Muhairi S.S., Poon L.L. Asymptomatic MERS-CoV infection in humans possibly linked to infected dromedaries imported from Oman to United Arab Emirates, May 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015;21:2197–2200. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chand K., Biswas S.K., Pandey A.B., Saxena A., Tewari N., Mondal B. A competitive ELISA for detection of group specific antibody to bluetongue virus using anti-core antibody. Biologicals. 2017;46:168–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

