Inhibition of Fosfomycin Resistance Protein FosA by Phosphonoformate (Foscarnet) in Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens
- PMID: 28993329
- PMCID: PMC5700359
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01424-17
Inhibition of Fosfomycin Resistance Protein FosA by Phosphonoformate (Foscarnet) in Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Pathogens
Abstract
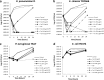
FosA proteins confer fosfomycin resistance to Gram-negative pathogens via glutathione-mediated modification of the antibiotic. In this study, we assessed whether inhibition of FosA by sodium phosphonoformate (PPF) (foscarnet), a clinically approved antiviral agent, would reverse fosfomycin resistance in representative Gram-negative pathogens. The inhibitory activity of PPF against purified recombinant FosA from Escherichia coli (FosA3), Klebsiella pneumoniae (FosAKP), Enterobacter cloacae (FosAEC), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (FosAPA) was determined by steady-state kinetic measurements. The antibacterial activity of PPF against FosA in clinical strains of these species was evaluated by susceptibility testing and time-kill assays. PPF increased the Michaelis constant (Km ) for fosfomycin in a dose-dependent manner, without affecting the maximum rate (Vmax) of the reaction, for all four FosA enzymes tested, indicating a competitive mechanism of inhibition. Inhibitory constant (Ki ) values were 22.6, 35.8, 24.4, and 56.3 μM for FosAKP, FosAEC, FosAPA, and FosA3, respectively. Addition of clinically achievable concentrations of PPF (∼667 μM) reduced the fosfomycin MICs by ≥4-fold among 52% of the K. pneumoniae, E. cloacae, and P. aeruginosa clinical strains tested and led to a bacteriostatic or bactericidal effect in time-kill assays among representative strains. PPF inhibits FosA activity across Gram-negative species and can potentiate fosfomycin activity against the majority of strains with chromosomally encoded fosA These data suggest that PPF may be repurposed as an adjuvant for fosfomycin to treat infections caused by some FosA-producing, multidrug-resistant, Gram-negative pathogens.
Keywords: Gram negative; fosfomycin; glutathione S-transferase; phosphonoformate.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
-
- Gupta K, Hooton TM, Naber KG, Wullt B, Colgan R, Miller LG, Moran GJ, Nicolle LE, Raz R, Schaeffer AJ, Soper DE. 2011. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: a 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin Infect Dis 52:e103–e120. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciq257. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wachino J, Yamane K, Suzuki S, Kimura K, Arakawa Y. 2010. Prevalence of fosfomycin resistance among CTX-M-producing Escherichia coli clinical isolates in Japan and identification of novel plasmid-mediated fosfomycin-modifying enzymes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:3061–3064. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01834-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

