Effects of Maraviroc versus Efavirenz in Combination with Zidovudine-Lamivudine on the CD4/CD8 Ratio in Treatment-Naive HIV-Infected Individuals
- PMID: 28993335
- PMCID: PMC5700350
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01763-17
Effects of Maraviroc versus Efavirenz in Combination with Zidovudine-Lamivudine on the CD4/CD8 Ratio in Treatment-Naive HIV-Infected Individuals
Abstract
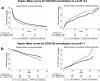
A low CD4/CD8 ratio during treated HIV infection reflects heightened immune activation and predicts death. The effects of different antiretroviral therapy regimens on CD4/CD8 ratio recovery remains unclear. We performed a post hoc analysis of the MERIT study, a randomized, double-blind trial of maraviroc versus efavirenz in combination with zidovudine-lamivudine in treatment-naive HIV-infected individuals. We found higher rates of CD4/CD8 ratio normalization with efavirenz, which was driven by a greater CD8+ T-cell decline.
Keywords: CD4/CD8 ratio; HIV; T cells; T-cell activation; antiretroviral therapy; efavirenz; maraviroc.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
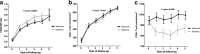
References
-
- Marcus JL, Chao CR, Leyden WA, Xu L, Quesenberry CP, Klein DB, Towner WJ, Horberg MA, Silverberg MJ. 2016. Narrowing the gap in life expectancy between HIV-infected and HIV-uninfected individuals with access to care. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 73:39–46. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000001014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tenorio AR, Zheng Y, Bosch RJ, Krishnan S, Rodriguez B, Hunt PW, Plants J, Seth A, Wilson CC, Deeks SG, Lederman MM, Landay AL. 2014. Soluble markers of inflammation and coagulation but not T-cell activation predict non-AIDS-defining morbid events during suppressive antiretroviral treatment. J Infect Dis 210:1248–1259. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu254. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sainz T, Serrano-Villar S, Díaz L, González-Tomé MI, Gurbindo MD, de José MI, Mellado MJ, Ramos JT, Zamora J, Moreno S, Muñoz-Fernández MA. 2013. The CD4/CD8 ratio as a marker T-cell activation, senescence and activation/exhaustion in treated HIV-infected children and young adults. AIDS 27:1513–1516. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32835faa72. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Serrano-Villar S, Sainz T, Lee SA, Hunt PW, Sinclair E, Shacklett BL, Ferre AL, Hayes TL, Somsouk M, Hsue PY, Van Natta ML, Meinert CL, Lederman MM, Hatano H, Jain V, Huang Y, Hecht FM, Martin JN, McCune JM, Moreno S, Deeks SG. 2014. HIV-infected individuals with low CD4/CD8 ratio despite effective antiretroviral therapy exhibit altered T cell subsets, heightened CD8+ T cell activation, and increased risk of non-AIDS morbidity and mortality. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004078. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004078. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

