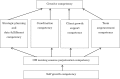
Competencies required for occupational health nurses
- PMID: 28993570
- PMCID: PMC5721278
- DOI: 10.1539/joh.16-0188-OA
Competencies required for occupational health nurses
Abstract
Objectives: For occupational health (OH) nurses to perform activities effectively, not only skills and knowledge but also competencies proposed by Dr. McClelland are indispensable. This study aimed to identify competencies required for OH nurses and to show their structure diagram.
Methods: Qualitative descriptive research was conducted from October 2010 to August 2011. Eight high-performing OH nurses participated, and data were collected from semi-structured interviews held for each nurse. Data were qualitatively and inductively analyzed using the KJ method.
Results: Seven competencies were identified: "self-growth competency," "OH nursing essence perpetuation competency," "strategic planning and duty fulfillment competency," "coordination competency," "client growth support competency," "team empowerment competency," and "creative competency." A structure diagram of the seven competencies was clarified. As the definitions of the competencies were different, the findings of competencies for OH nursing in the United States of America (USA) could not simply be compared with the findings of our study; however, all seven competencies were compatible with those in AAOHN model 1 and AAOHN model 2 in the USA.
Conclusion: Our seven competencies are essential for OH nurses to perform activities that meet the expectations of employees and the employer.
Keywords: Competency; Occupational health nurse; Occupational health nursing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kato T, Kono K, Tomiyama A, et al. Continuing professional education for OH nurses in Japan. J UOE 1998; 20: 102-106.
-
- Spencer L, Spencer S. Competence at work: Models for Superior Performance. New York: Wiley; 1993. p. 9.
-
- Aihara T. Thinking about competencies: Competency and human resource development. Nouryoku Kaihatsu 1999; 20: 18-21. (in Japanese).
-
- Nakayama Y, Kudo M, Ishihara M. A study of measurement scale and developmental process of competence in nursing practice. Grants-in-aid for Scientific Research (Foundation Research A). [Online]. 2010[cited 2016 Jun. 2]; Available from: URL: https://kaken.nii.ac.jp/ja/report/KAKENHI-PROJECT-18209062/RECORD-182090... (in Japanese).
-
- Kamiya M, Endo K, Okazaki M. The nurses' focus of viewpoints for promoting team medical care, discuss for critical competencies of nurses in collaboration. The 30th Nihon Kango Kagaku Gakkai Gakujutsusyukai Kouensyu 2010; 270. (in Japanese).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials