Electroencephalography in the Diagnosis of Genetic Generalized Epilepsy Syndromes
- PMID: 28993753
- PMCID: PMC5622315
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00499
Electroencephalography in the Diagnosis of Genetic Generalized Epilepsy Syndromes
Abstract
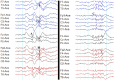
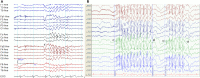
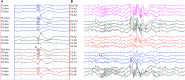
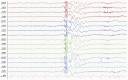
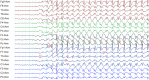
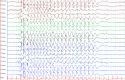
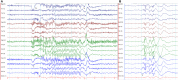
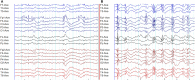
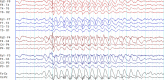
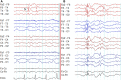
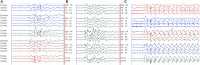
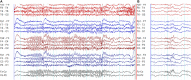
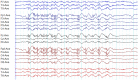
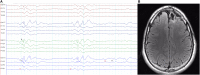
Genetic generalized epilepsy (GGE) consists of several syndromes diagnosed and classified on the basis of clinical features and electroencephalographic (EEG) abnormalities. The main EEG feature of GGE is bilateral, synchronous, symmetric, and generalized spike-wave complex. Other classic EEG abnormalities are polyspikes, epileptiform K-complexes and sleep spindles, polyspike-wave discharges, occipital intermittent rhythmic delta activity, eye-closure sensitivity, fixation-off sensitivity, and photoparoxysmal response. However, admixed with typical changes, atypical epileptiform discharges are also commonly seen in GGE. There are circadian variations of generalized epileptiform discharges. Sleep, sleep deprivation, hyperventilation, intermittent photic stimulation, eye closure, and fixation-off are often used as activation techniques to increase the diagnostic yield of EEG recordings. Reflex seizure-related EEG abnormalities can be elicited by the use of triggers such as cognitive tasks and pattern stimulation during the EEG recording in selected patients. Distinct electrographic abnormalities to help classification can be identified among different electroclinical syndromes.
Keywords: absence seizure; circadian; myoclonic seizure; photoparoxysmal response; polyspike; sleep; spike-wave; tonic-clonic seizure.
Figures

References
-
- Berg AT, Berkovic SF, Brodie MJ, Buchhalter J, Cross JH, van Emde Boas W, et al. Revised terminology and concepts for organization of seizures and epilepsies: report of the ILAE Commission on Classification and Terminology, 2005–2009. Epilepsia (2010) 51(4):676–85. 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2010.02522.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

