Human Cytomegalovirus Delays Neutrophil Apoptosis and Stimulates the Release of a Prosurvival Secretome
- PMID: 28993776
- PMCID: PMC5622148
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01185
Human Cytomegalovirus Delays Neutrophil Apoptosis and Stimulates the Release of a Prosurvival Secretome
Abstract
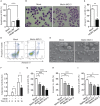
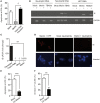
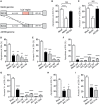
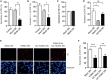
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a major cause of viral disease in the young and the immune-suppressed. At sites of infection, HCMV recruits the neutrophil, a cell with a key role in orchestrating the initial immune response. Herein, we report a profound survival response in human neutrophils exposed to the clinical HCMV isolate Merlin, but not evident with the attenuated strain AD169, through suppression of apoptosis. The initial survival event, which is independent of viral gene expression and involves activation of the ERK/MAPK and NF-κB pathways, is augmented by HCMV-stimulated release of a secretory cytokine profile that further prolongs neutrophil lifespan. As aberrant neutrophil survival contributes to tissue damage, we predict that this may be relevant to the immune pathology of HCMV, and the presence of this effect in clinical HCMV strains and its absence in attenuated strains implies a beneficial effect to the virus in pathogenesis and/or dissemination. In addition, we show that HCMV-exposed neutrophils release factors that enhance monocyte recruitment and drive monocyte differentiation to a HCMV-permissive phenotype in an IL-6-dependent manner, thus providing an ideal vehicle for viral dissemination. This study increases understanding of HCMV-neutrophil interactions, highlighting the potential role of neutrophil recruitment as a virulence mechanism to promote HCMV pathology in the host and influence the dissemination of HCMV infection. Targeting these mechanisms may lead to new antiviral strategies aimed at limiting host damage and inhibiting viral spread.
Keywords: apoptosis; human cytomegalovirus; monocyte; neutrophil; polymorphonuclear leukocyte.
Figures



References
-
- Watson RW, Rotstein OD, Nathens AB, Parodo J, Marshall JC. Neutrophil apoptosis is modulated by endothelial transmigration and adhesion molecule engagement. J Immunol (1997) 158(2):945–53. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

