MIFuzzy Clustering for Incomplete Longitudinal Data in Smart Health
- PMID: 28993813
- PMCID: PMC5631546
- DOI: 10.1016/j.smhl.2017.04.002
MIFuzzy Clustering for Incomplete Longitudinal Data in Smart Health
Abstract
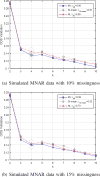
Missing data are common in longitudinal observational and randomized controlled trials in smart health studies. Multiple-imputation based fuzzy clustering is an emerging non-parametric soft computing method, used for either semi-supervised or unsupervised learning. Multiple imputation (MI) has been widely-used in missing data analyses, but has not yet been scrutinized for unsupervised learning methods, although they are important for explaining the heterogeneity of treatment effects. Built upon our previous work on MIfuzzy clustering, this paper introduces the MIFuzzy concepts and performance, theoretically, empirically and numerically demonstrate how MI-based approach can reduce the uncertainty of clustering accuracy in comparison to non- and single-imputation based clustering approach. This paper advances our understanding of the utility and strength of MIFuzzy clustering approach to processing incomplete longitudinal behavioral intervention data.
Keywords: Fuzzy clustering; MIFuzzy; Missing values; Multiple imputation; longitudinal data.
Figures

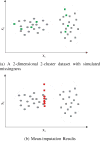
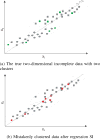
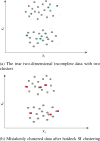
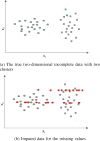
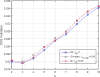
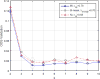
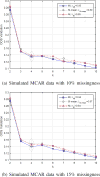
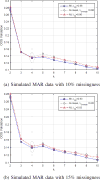
Similar articles
-
Topic modeling for systematic review of visual analytics in incomplete longitudinal behavioral trial data.Smart Health (Amst). 2020 Nov;18:100142. doi: 10.1016/j.smhl.2020.100142. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Smart Health (Amst). 2020. PMID: 33344744 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple- vs Non- or Single-Imputation based Fuzzy Clustering for Incomplete Longitudinal Behavioral Intervention Data.IEEE Int Conf Connect Health Appl Syst Eng Technol. 2016 Jun;2016:219-228. doi: 10.1109/CHASE.2016.19. Epub 2016 Aug 18. IEEE Int Conf Connect Health Appl Syst Eng Technol. 2016. PMID: 29034067 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Imputation based Clustering Validation (MIV) for Big Longitudinal Trial Data with Missing Values in eHealth.J Med Syst. 2016 Jun;40(6):146. doi: 10.1007/s10916-016-0499-0. Epub 2016 Apr 28. J Med Syst. 2016. PMID: 27126063 Free PMC article.
-
Introduction to multiple imputation for dealing with missing data.Respirology. 2014 Feb;19(2):162-167. doi: 10.1111/resp.12226. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Respirology. 2014. PMID: 24372814 Review.
-
Multiple Imputation for Incomplete Data in Environmental Epidemiology Research.Curr Environ Health Rep. 2019 Jun;6(2):62-71. doi: 10.1007/s40572-019-00230-y. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2019. PMID: 31090043 Review.
Cited by
-
Feature Interaction Detection in Big Data Through a New Choquet Integral based Deep Neural Network.Proc IEEE Int Conf Big Data. 2024 Dec;2024:700-708. doi: 10.1109/bigdata62323.2024.10825719. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Proc IEEE Int Conf Big Data. 2024. PMID: 40291853 Free PMC article.
-
Topic modeling for systematic review of visual analytics in incomplete longitudinal behavioral trial data.Smart Health (Amst). 2020 Nov;18:100142. doi: 10.1016/j.smhl.2020.100142. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Smart Health (Amst). 2020. PMID: 33344744 Free PMC article.
-
Acculturation, Depression, and Smoking Cessation: a trajectory pattern recognition approach.Tob Induc Dis. 2017 Jul 24;15:33. doi: 10.1186/s12971-017-0135-x. eCollection 2017. Tob Induc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28747857 Free PMC article.
-
Federated Fuzzy Clustering for Decentralized Incomplete Longitudinal Behavioral Data.IEEE Internet Things J. 2024 Apr 15;11(8):14657-14670. doi: 10.1109/jiot.2023.3343719. Epub 2023 Dec 18. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024. PMID: 38605934 Free PMC article.
-
eFCM: An Enhanced Fuzzy C-Means Algorithm for Longitudinal Intervention Data.Int Conf Comput Netw Commun. 2018 Mar;2018:912-916. doi: 10.1109/ICCNC.2018.8390419. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Int Conf Comput Netw Commun. 2018. PMID: 30906794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sawicki P, Didjurgeit U, Mühlhauser I, Berger M. Behaviour therapy versus doctor’s anti-smoking advice in diabetic patients. Journal of internal medicine. 1993;234(4):407–409. - PubMed
-
- Marlow SP, Stoller JK. Smoking cessation. Respiratory care. 2003;48(12):1238–1256. - PubMed
-
- Mottillo S, Filion KB, Bélisle P, Joseph L, Gervais A, O’Loughlin J, Paradis G, Pihl R, Pilote L, Rinfret S, et al. Behavioural interventions for smoking cessation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. European heart journal. 2009;30(6):718–730. - PubMed
-
- Barth J, Bengel J, Critchley J. Efficacy of psychosocial interventions for smoking cessation in patients with coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of Behavioral Medicine. 2006;32(1):10–20. - PubMed
-
- Hennrikus DJ, Lando HA, McCarty MC, Klevan D, Holtan N, Huebsch JA, Jestus S, Pentel PR, Pine D, Sullivan S, et al. The team project: the effectiveness of smoking cessation intervention with hospital patients. Preventive medicine. 2005;40(3):249–258. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
