Effects of Acetylcholine on β-Amyloid-Induced cPLA2 Activation in the TB Neuroectodermal Cell Line: Implications for the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 28993924
- PMCID: PMC11481997
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-017-0555-4
Effects of Acetylcholine on β-Amyloid-Induced cPLA2 Activation in the TB Neuroectodermal Cell Line: Implications for the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
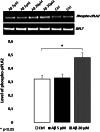
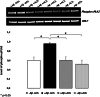
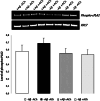
The role of β-amyloid (Aβ) in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is still considered crucial. The state of Aβ aggregation is critical in promoting neuronal loss and neuronal function impairment. Recently, we demonstrated that Acetylcholine (ACh) is neuroprotective against the toxic effects of Aβ in the cholinergic LAN-2 cells. In biophysical experiments, ACh promotes the soluble Aβ peptide conformation rather than the aggregation-prone β-sheet conformation. In order to better understand the biological role of ACh in AD, we studied the effect of Aβ on the phosphorylation of the cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) in the TB neuroectodermal cell line, which differentiates toward a neuronal phenotype when cultured in the presence of retinoic acid (RA). We chose the phosphorylated form of cPLA2 (Ser505, Phospho-cPLA2) as a biomarker to test the influence of ACh on the effects of Aβ in both undifferentiated and RA-differentiated TB cells. Our results show that TB cells are responsive to Aβ. Moreover, in undifferentiated cells 1 h treatment with Aβ induces a 2.5-fold increase of the Phospho-cPLA2 level compared to the control after 24 h in vitro, while no significant difference is observed between Aβ-treated and non-treated cells after 4 and 7 days in vitro. The RA-differentiated cells are not sensitive to Aβ. In TB cell line ACh is able to blunt the effects of Aβ. The ability of ACh to protect non-cholinergic cells against Aβ reinforces the hypothesis that, in addition to its role in cholinergic transmission, ACh could also act as a neuroprotective agent.
Keywords: Acetylcholine; Alzheimer’s disease; Differentiation; Phospholipase A2; TB cell line; β-Amyloid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no personal or institutional conflict of interest related to the presented research and its publication.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of cytosolic phospholipase A2 α in amyloid precursor protein induction by amyloid beta1-42 : implication for neurodegeneration.J Neurochem. 2015 Mar;132(5):559-71. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13012. Epub 2015 Feb 3. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25533654
-
β-Amyloid-acetylcholine molecular interaction: new role of cholinergic mediators in anti-Alzheimer therapy?Future Med Chem. 2016 Jul;8(11):1179-89. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2016-0006. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Future Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27402297
-
Amyloid beta enhances cytosolic phospholipase A2 level and arachidonic acid release via nitric oxide in APP-transfected PC12 cells.Acta Biochim Pol. 2007;54(3):611-23. Epub 2007 Aug 23. Acta Biochim Pol. 2007. PMID: 17713604
-
Mechanistic Insight into the Design of Chemical Tools to Control Multiple Pathogenic Features in Alzheimer's Disease.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Oct 19;54(20):3930-3940. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00457. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34606227 Review.
-
Interactions between beta-amyloid and central cholinergic neurons: implications for Alzheimer's disease.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2004 Nov;29(6):427-41. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15644984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Royal Jelly as an Intelligent Anti-Aging Agent-A Focus on Cognitive Aging and Alzheimer's Disease: A Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Sep 29;9(10):937. doi: 10.3390/antiox9100937. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33003559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring Mannosylpurines as Copper Chelators and Cholinesterase Inhibitors with Potential for Alzheimer's Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 30;16(1):54. doi: 10.3390/ph16010054. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36678552 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding How Physical Exercise Improves Alzheimer's Disease: Cholinergic and Monoaminergic Systems.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 May 18;14:869507. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.869507. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35663578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutrition and cognition across the lifetime: an overview on epigenetic mechanisms.AIMS Neurosci. 2021 Jul 15;8(4):448-476. doi: 10.3934/Neuroscience.2021024. eCollection 2021. AIMS Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34877399 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abramov AY, Canevari L, Duchen MR (2004) Calcium signals induced by amyloid β peptide and their consequences in neurons and astrocytes in culture. Biochimica et Biophys Acta 1742:81–87 - PubMed
-
- Bartus RT (2000) On neurodegenerative diseases, models, and treatment strategies: lessons learned and lessons forgotten a generation following the cholinergic hypothesis. Exp Neurol 163:495–529 - PubMed
-
- Bate C, Williams A (2010) Amyloid-β1–40 inhibits amyloid-β1–42 induced activation of cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 and synapse degeneration. J Alzheimer’s Dis 21:985–993 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

