MTRR A66G, RFC1 G80A, and MTHFR C677T and A1298C Polymorphisms and Disease Activity in Mexicans with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Methotrexate
- PMID: 28994615
- PMCID: PMC5695735
- DOI: 10.1089/gtmb.2017.0124
MTRR A66G, RFC1 G80A, and MTHFR C677T and A1298C Polymorphisms and Disease Activity in Mexicans with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Methotrexate
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the relationships of polymorphisms in genes whose protein products are related in the metabolic pathway of folic acid, particularly MTRR A66G, RFC1 G80A, and MTHFR C677T and A1298C, and disease activity in Mexican patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treated with methotrexate (MTX).
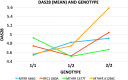
Materials and methods: Sixty-eight patients with RA were included in the study who were being treated with MTX, either with or without other drugs. In addition to general data, disease activity was measured by the disease activity score 28 (DAS28). Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) genotyping was performed by allelic discrimination using real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results: Differences in genotype (homozygotic or heterozygotic for each allele), allele distributions, and phenotype were not statistically different between the RA group and control populations. We did not find any association between the studied polymorphisms and disease activity nor with the intragroup variables (e.g., clinical activity, body mass index, and single- or combined-drug treatment) or between genetic markers; we also did not find any association within the RA group or between the RA group and control populations.
Conclusion: Additional studies of more polymorphisms related to this or other metabolic pathways are required to determine the influence of genetics on disease activity in RA.
Keywords: DAS28; MTHFR; MTRR; RFC1; methotrexate; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, et al. (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324 - PubMed
-
- Barrera Cruz A, Beltran Castillo J, Blanco Favela F, et al. (2010) Diagnóstico y Tratamiento de Artritis Reumatoide del Adulto. México: Secretaria de Salud
-
- Boughrara W, Aberkane M, Fodil M, et al. (2015) Impact of MTHFR rs1801133, MTHFR rs1801131 and ABCB1 rs1045642 polymorphisms with increased susceptibility of rheumatoid arthritis in the West Algerian population: a case-control study. Acta Reumatol Port 40:363–371 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
