Improved Method for the Establishment of an In Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Model Based on Porcine Brain Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 28994773
- PMCID: PMC5752332
- DOI: 10.3791/56277
Improved Method for the Establishment of an In Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Model Based on Porcine Brain Endothelial Cells
Abstract
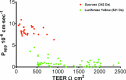
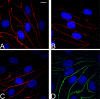
The aim of this protocol presents an optimized procedure for the purification and cultivation of pBECs and to establish in vitro blood-brain barrier (BBB) models based on pBECs in mono-culture (MC), MC with astrocyte-conditioned medium (ACM), and non-contact co-culture (NCC) with astrocytes of porcine or rat origin. pBECs were isolated and cultured from fragments of capillaries from the brain cortices of domestic pigs 5-6 months old. These fragments were purified by careful removal of meninges, isolation and homogenization of grey matter, filtration, enzymatic digestion, and centrifugation. To further eliminate contaminating cells, the capillary fragments were cultured with puromycin-containing medium. When 60-95% confluent, pBECs growing from the capillary fragments were passaged to permeable membrane filter inserts and established in the models. To increase barrier tightness and BBB characteristic phenotype of pBECs, the cells were treated with the following differentiation factors: membrane permeant 8-CPT-cAMP (here abbreviated cAMP), hydrocortisone, and a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, RO-20-1724 (RO). The procedure was carried out over a period of 9-11 days, and when establishing the NCC model, the astrocytes were cultured 2-8 weeks in advance. Adherence to the described procedures in the protocol has allowed the establishment of endothelial layers with highly restricted paracellular permeability, with the NCC model showing an average transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER) of 1249 ± 80 Ω cm2, and paracellular permeability (Papp) for Lucifer Yellow of 0.90 10-6 ± 0.13 10-6 cm sec-1 (mean ± SEM, n=55). Further evaluation of this pBEC phenotype showed good expression of the tight junctional proteins claudin 5, ZO-1, occludin and adherens junction protein p120 catenin. The model presented can be used for a range of studies of the BBB in health and disease and, with the highly restrictive paracellular permeability, this model is suitable for studies of transport and intracellular trafficking.
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Rönnbäck L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nature Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(1):41–53. - PubMed
-
- Hawkins BT, Davis TP. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57(2):173–185. - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ. Anatomy and Physiology of the Blood-Brain Barriers. Drug Delivery to the Brain SE - 1. 2014;10:3–21.
-
- Igarashi Y, et al. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor induces barrier function of endothelial cells forming the blood-brain barrier. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;261(1):108–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials