Blinatumomab-induced lineage switch of B-ALL with t(4:11)(q21;q23) KMT2A/AFF1 into an aggressive AML: pre- and post-switch phenotypic, cytogenetic and molecular analysis
- PMID: 29016570
- PMCID: PMC5637108
- DOI: 10.1038/bcj.2017.89
Blinatumomab-induced lineage switch of B-ALL with t(4:11)(q21;q23) KMT2A/AFF1 into an aggressive AML: pre- and post-switch phenotypic, cytogenetic and molecular analysis
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Mark Litzow receives research support for clinical trials from Amgen. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
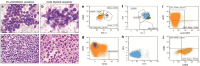
Figures
References
-
- Stass S, Mirro J, Melvin S, Pui CH, Murphy SB, Williams D. Lineage switch in acute leukemia. Blood 1984; 64: 701–706. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann P, Hofmeister R, Brischwein K, Brandl C, Crommer S, Bargou R et al. Serial killing of tumor cells by cytotoxic T cells redirected with a CD19-/CD3-bispecific single-chain antibody construct. Int J Cancer 2005; 115: 98–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

