TLR2/TLR4 activation induces Tregs and suppresses intestinal inflammation caused by Fusobacterium nucleatum in vivo
- PMID: 29016688
- PMCID: PMC5633168
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186179
TLR2/TLR4 activation induces Tregs and suppresses intestinal inflammation caused by Fusobacterium nucleatum in vivo
Abstract
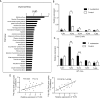
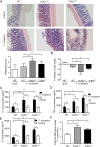
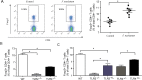
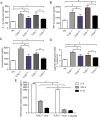
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) 2 and 4 play critical roles in intestinal inflammation caused by Fusobacterium nucleatum (F. nucleatum) infection, but the role of TLR2/TLR4 in regulation of proinflammatory cytokines remains unknown. In this study, through microarray analysis and qRT-PCR, we showed that TLR2/TLR4 are involved in the F. nucleatum-induced inflammatory signaling pathway in Caco-2 cells, C57BL/6 mice and human clinical specimens. In TLR2-/- and TLR4-/- mice, F. nucleatum infection resulted in increased colonization of the bacteria and production of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-8, IL-1β and TNF-α. In addition, the ratio of Foxp3+ CD4+ T cells in the total CD4+ T cells in TLR2-/- and TLR4-/- mice was less than that in wild-type mice, and the ratio in hybrid mice was more than that in knockout mice, which suggested that TLR2/TLR4 mediated the number of Tregs. Furthermore, it was observed that inflammatory cytokine levels were reduced in TLR2-/- mice after Treg transfer. Thus, these data indicate that TLR2/TLR4 regulate F. nucleatum-induced inflammatory cytokines through Tregs in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Allen-Vercoe E, Strauss J, Chadee K. Fusobacterium nucleatum: an emerging gut pathogen? Gut Microbes. 2011;2(5):294–8. Epub 2011/11/10. doi: 10.4161/gmic.2.5.18603 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jess T, Rungoe C, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Risk of colorectal cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10(6):639–45. Epub 2012/02/01. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2012.01.010 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Redline RW, Han YW. Fusobacterium nucleatum induces fetal death in mice via stimulation of TLR4-mediated placental inflammatory response. J Immunol. 2007;179(4):2501–8. Epub 2007/08/07. . - PubMed
-
- Kostic AD, Chun E, Robertson L, Glickman JN, Gallini CA, Michaud M, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor-immune microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe. 2013;14(2):207–15. Epub 2013/08/21. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.07.007 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3772512. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sears CL, Garrett WS. Microbes, microbiota, and colon cancer. Cell Host Microbe. 2014;15(3):317–28. Epub 2014/03/19. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.02.007 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4003880. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

