Molecular differences in IDH wildtype glioblastoma according to MGMT promoter methylation
- PMID: 29016808
- PMCID: PMC5817966
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nox160
Molecular differences in IDH wildtype glioblastoma according to MGMT promoter methylation
Abstract
Background: O6-methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation status is a predictive biomarker in glioblastoma. We investigated whether this marker furthermore defines a molecularly distinct tumor subtype with clinically different outcome.
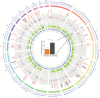
Methods: We analyzed copy number variation (CNV) and methylation profiles of 1095 primary and 92 progressive isocitrate dehydrogenase wildtype glioblastomas, including paired samples from 49 patients. DNA mutation data from 182 glioblastoma samples of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and RNA expression from 107 TCGA and 55 Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas samples were analyzed.
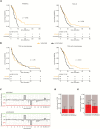
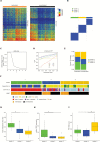
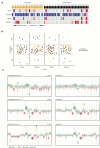
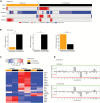
Results: Among untreated glioblastomas, MGMT promoter methylated (mMGMT) and unmethylated (uMGMT) tumors did not show different CNV or specific gene mutations, but a higher mutation count in mMGMT tumors. We identified 3 methylation clusters. Cluster 1 showed the highest average methylation and was enriched for mMGMT tumors. Seventeen genes including gastrulation brain homeobox 2 (GBX2) were found to be hypermethylated and downregulated on the mRNA level in mMGMT tumors. In progressive glioblastomas, platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) and GLI2 amplifications were enriched in mMGMT tumors. Methylated MGMT tumors gain PDGFRA amplification of PDGFRA, whereas uMGMT tumors with amplified PDGFRA frequently lose this amplification upon progression. Glioblastoma patients surviving <6 months and with mMGMT harbored less frequent epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) amplifications, more frequent TP53 mutations, and a higher tumor necrosis factor-nuclear factor-kappaB (TNF-NFκB) pathway activation compared with patients surviving >12 months.
Conclusions: MGMT promoter methylation status does not define a molecularly distinct glioblastoma subpopulation among untreated tumors. Progressive mMGMT glioblastomas and mMGMT tumors of patients with short survival tend to have more unfavorable molecular profiles.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com
Figures

References
-
- Omuro A, DeAngelis LM. Glioblastoma and other malignant gliomas: a clinical review. JAMA. 2013;310(17):1842–1850. - PubMed
-
- Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G et al. . The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131(6):803–820. - PubMed
-
- Wick W, Weller M, van den Bent M et al. . MGMT testing–the challenges for biomarker-based glioma treatment. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014;10(7):372–385. - PubMed
-
- Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T et al. . MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):997–1003. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ et al. ; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987–996. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

