Phase I/II trial of vorinostat combined with temozolomide and radiation therapy for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: results of Alliance N0874/ABTC 02
- PMID: 29016887
- PMCID: PMC5909661
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nox161
Phase I/II trial of vorinostat combined with temozolomide and radiation therapy for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: results of Alliance N0874/ABTC 02
Abstract
Background: Vorinostat, a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, has shown radiosensitizing properties in preclinical studies. This open-label, single-arm trial evaluated the maximum tolerated dose (MTD; phase I) and efficacy (phase II) of vorinostat combined with standard chemoradiation in newly diagnosed glioblastoma.
Methods: Patients received oral vorinostat (300 or 400 mg/day) on days 1-5 weekly during temozolomide chemoradiation. Following a 4- to 6-week rest, patients received up to 12 cycles of standard adjuvant temozolomide and vorinostat (400 mg/day) on days 1-7 and 15-21 of each 28-day cycle. Association between vorinostat response signatures and progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) was assessed based on RNA sequencing of baseline tumor tissue.
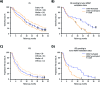
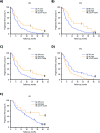
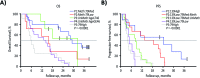
Results: Phase I and phase II enrolled 15 and 107 patients, respectively. The combination therapy MTD was vorinostat 300 mg/day and temozolomide 75 mg/m2/day. Dose-limiting toxicities were grade 4 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia and grade 3 aspartate aminotransferase elevation, hyperglycemia, fatigue, and wound dehiscence. The primary efficacy endpoint in the phase II cohort, OS rate at 15 months, was 55.1% (median OS 16.1 mo), and consequently, the study did not meet its efficacy objective. Most common treatment-related grade 3/4 toxicities in the phase II component were lymphopenia (32.7%), thrombocytopenia (28.0%), and neutropenia (21.5%). RNA expression profiling of baseline tumors (N = 76) demonstrated that vorinostat resistance (sig-79) and sensitivity (sig-139) signatures had a reverse and positive association with OS/PFS, respectively.
Conclusions: Vorinostat combined with standard chemoradiation had acceptable tolerability in newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Although the primary efficacy endpoint was not met, vorinostat sensitivity and resistance signatures could facilitate patient selection in future trials.
Figures
References
-
- Chinot OL, Wick W, Mason W et al. Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(8):709–722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

