Impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on in-hospital-mortality after major cardiovascular events in Spain (2002-2014)
- PMID: 29017514
- PMCID: PMC5635492
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-017-0609-4
Impact of type 2 diabetes mellitus on in-hospital-mortality after major cardiovascular events in Spain (2002-2014)
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus has long been associated with cardiovascular events. Nevertheless, the higher burden of traditional cardiovascular risk factors reported in high-income countries is offset by a more widespread use of preventive measures and revascularization or other invasive procedures. The aim of this investigation is to describe trends in number of cases and outcomes, in-hospital mortality (IHM) and length of hospital stay (LHS), of hospital admissions for major cardiovascular events between type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and matched non-diabetes patients.
Methods: Retrospective study using National Hospital Discharge Database, analyzed in 4 years 2002, 2006, 2010, 2014, in Spain. We included patients (≥ 40 years old) with a primary diagnosis of myocardial infarction, ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, aortic aneurysm and dissection and acute lower limb ischemia in people with T2DM. Cases were matched with controls (without T2DM) by ICD-9-CM codes, sex, age, province of residence and year.
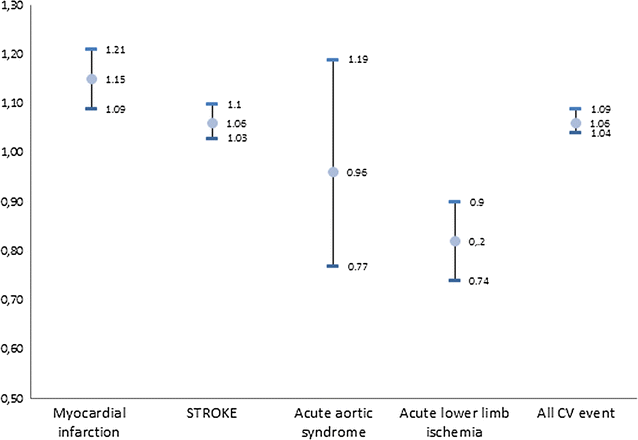
Results: We selected 130,011 matched couples (50,427 with myocardial infarction, 60,236 with stroke, 2599 with aortic aneurysm and dissection and 16,749 with acute lower limb ischemia. Among T2DM patients we found increasing numbers of admissions overtime for stroke (10,794 in 2002 vs 17,559 in 2014), aortic aneurysm and dissection (390 vs 841) and acute lower limb ischemia (3854 vs. 4548). People were progressively older (except for myocardial infarction), had more comorbidities (especially T2DM patients), and were more frequently coded overtime for cardiovascular risk factors (smoking, obesity, hypertension, lipid disorders) and renal diseases. LHS and IHM declined overtime, though IHM only did it significantly in T2DM patients. Multivariable adjustment showed that T2DM patients had a significantly 15% higher mortality rate during admission for myocardial infarction, a 6% higher mortality for stroke, and a 6% higher mortality rate for "all cardiovascular events combined", than non-diabetic matched controls.
Conclusions: The number of hospital admissions for stroke, aortic aneurysm and dissection and acute lower limb ischemia increased overtime, but remained stable for myocardial infarction. T2DM is associated to higher IHM after major cardiovascular events. Further research is needed to help us understand the reasons for an apparently increased mortality in T2DM patients when admitted to hospital for some major cardiovascular events.
Keywords: Acute lower limb ischemia; Acute myocardial infarction; Aortic aneurysm and dissection; In-hospital mortality; Stroke; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
References
-
- Lopez-de-Andres A, Jimenez-Garcia R, Hernandez-Barrera V, Jimenez-Trujillo I, Gallardo-Pino C, de Miguel AG, Carrasco-Garrido P. National trends over one decade in hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction among Spanish adults with type 2 diabetes: cumulative incidence, outcomes and use of percutaneous coronary intervention. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e85697. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085697. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical