Neuronal SIRT1 (Silent Information Regulator 2 Homologue 1) Regulates Glycolysis and Mediates Resveratrol-Induced Ischemic Tolerance
- PMID: 29018134
- PMCID: PMC5654689
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.018562
Neuronal SIRT1 (Silent Information Regulator 2 Homologue 1) Regulates Glycolysis and Mediates Resveratrol-Induced Ischemic Tolerance
Abstract
Background and purpose: Resveratrol, at least in part via SIRT1 (silent information regulator 2 homologue 1) activation, protects against cerebral ischemia when administered 2 days before injury. However, it remains unclear if SIRT1 activation must occur, and in which brain cell types, for the induction of neuroprotection. We hypothesized that neuronal SIRT1 is essential for resveratrol-induced ischemic tolerance and sought to characterize the metabolic pathways regulated by neuronal Sirt1 at the cellular level in the brain.
Methods: We assessed infarct size and functional outcome after transient 60 minute middle cerebral artery occlusion in control and inducible, neuronal-specific SIRT1 knockout mice. Nontargeted primary metabolomics analysis identified putative SIRT1-regulated pathways in brain. Glycolytic function was evaluated in acute brain slices from adult mice and primary neuronal-enriched cultures under ischemic penumbra-like conditions.
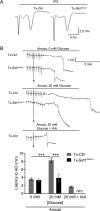
Results: Resveratrol-induced neuroprotection from stroke was lost in neuronal Sirt1 knockout mice. Metabolomics analysis revealed alterations in glucose metabolism on deletion of neuronal Sirt1, accompanied by transcriptional changes in glucose metabolism machinery. Furthermore, glycolytic ATP production was impaired in acute brain slices from neuronal Sirt1 knockout mice. Conversely, resveratrol increased glycolytic rate in a SIRT1-dependent manner and under ischemic penumbra-like conditions in vitro.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrate that resveratrol requires neuronal SIRT1 to elicit ischemic tolerance and identify a novel role for SIRT1 in the regulation of glycolytic function in brain. Identification of robust neuroprotective mechanisms that underlie ischemia tolerance and the metabolic adaptations mediated by SIRT1 in brain are crucial for the translation of therapies in cerebral ischemia and other neurological disorders.
Keywords: brain; glucose; metabolomics; neuroprotection; resveratrol; sirtuin 1; stroke.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Resveratrol Preconditioning Induces a Novel Extended Window of Ischemic Tolerance in the Mouse Brain.Stroke. 2015 Aug;46(8):2293-8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.009876. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Stroke. 2015. PMID: 26159789 Free PMC article.
-
A dietary polyphenol resveratrol acts to provide neuroprotection in recurrent stroke models by regulating AMPK and SIRT1 signaling, thereby reducing energy requirements during ischemia.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 May;37(10):1669-81. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12162. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. Retraction in: Eur J Neurosci. 2016 Apr;43(7):990. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13230. PMID: 23461657 Retracted.
-
Resveratrol pretreatment protects rat brain from cerebral ischemic damage via a sirtuin 1-uncoupling protein 2 pathway.Neuroscience. 2009 Mar 31;159(3):993-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.01.017. Epub 2009 Jan 19. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19356683 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol and ischemic preconditioning in the brain.Curr Med Chem. 2008;15(15):1545-51. doi: 10.2174/092986708784638861. Curr Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18537630 Review.
-
New role of silent information regulator 1 in cerebral ischemia.Neurobiol Aging. 2013 Dec;34(12):2879-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.06.008. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Neurobiol Aging. 2013. PMID: 23855981 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of oleuropein on the brain tissue in D-Galactose-induced aging in rat model.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Dec 20;52(1):67. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10165-9. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39704928
-
Emerging immune and cell death mechanisms in stroke: Saponins as therapeutic candidates.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020 Oct 3;9:100152. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2020.100152. eCollection 2020 Dec. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2020. PMID: 34589895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective potential for mitigating ischemia-reperfusion-induced damage.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Aug 1;20(8):2199-2217. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01985. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 39104164 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 prevents noise-induced hearing loss by enhancing cochlear mitochondrial function.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Apr 2;23(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02152-9. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40176044 Free PMC article.
-
NAD+ precursor nutritional supplements sensitize the brain to future ischemic events.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2023 Nov;43(2_suppl):37-48. doi: 10.1177/0271678X231156500. Epub 2023 Feb 22. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2023. PMID: 37434361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Writing Group M, Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: A report from the american heart association. Circulation. 2016;133:e38–360. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

