High Reflectance Nanoscale V/Sc Multilayer for Soft X-ray Water Window Region
- PMID: 29018232
- PMCID: PMC5635135
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-13222-5
High Reflectance Nanoscale V/Sc Multilayer for Soft X-ray Water Window Region
Abstract
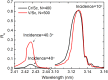
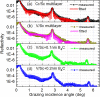
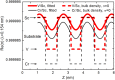
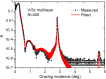
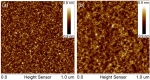
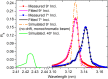
V/Sc multilayer is experimentally demonstrated for the first time as a high reflectance mirror for the soft X-ray water window region. It primarily works at above the Sc-L edge (λ = 3.11 nm) under near normal incidence while a second peak appears at above the V-L edge (λ = 2.42 nm) under grazing incidence. The V/Sc multilayer fabricated with a d-spacing of 1.59 nm and 30 bilayers has a smaller interface width (σ = 0.27 and 0.32 nm) than the conventional used Cr/Sc (σ = 0.28 and 0.47 nm). For V/Sc multilayer with 30 bilayers, the introduction of B4C barrier layers has little improvement on the interface structure. As the number of bilayers increasing to 400, the growth morphology and microstructure of the V/Sc layers evolves with slightly increased crystallization. Nevertheless, the surface roughness remains to be 0.25 nm. A maximum soft X-ray reflectance of 18.4% is measured at λ = 3.129 nm at 9° off-normal incidence using the 400-bilayers V/Sc multilayer. According to the fitted model, an s-polarization reflectance of 5.2% can also be expected at λ = 2.425 nm under 40° incidence. Based on the promising experimental results, further improvement of the reflectance can be achieved by using a more stable deposition system, exploring different interface engineering methods and so on.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High reflectance Cr/V multilayer with B(4)C barrier layer for water window wavelength region.Opt Lett. 2016 Feb 15;41(4):701-4. doi: 10.1364/OL.41.000701. Opt Lett. 2016. PMID: 26872167
-
14.5% near-normal incidence reflectance of Cr/Sc x-ray multilayer mirrors for the water window.Opt Lett. 2003 Dec 15;28(24):2494-6. doi: 10.1364/ol.28.002494. Opt Lett. 2003. PMID: 14690125
-
High-reflectance magnetron-sputtered scandium-based x-ray multilayer mirrors for the water window.Opt Lett. 2017 May 15;42(10):1927-1930. doi: 10.1364/OL.42.001927. Opt Lett. 2017. PMID: 28504761
-
Optimization of Cr/Sc-based multilayer mirrors for water window soft x-rays.Opt Lett. 2024 Jun 15;49(12):3420-3423. doi: 10.1364/OL.523431. Opt Lett. 2024. PMID: 38875635
-
Impact of B4C co-sputtering on structure and optical performance of Cr/Sc multilayer X-ray mirrors.Opt Express. 2017 Jul 24;25(15):18274-18287. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.018274. Opt Express. 2017. PMID: 28789315
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

