When is macular edema not macular edema? An update on macular telangiectasia type 2
- PMID: 29018690
- PMCID: PMC5602132
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tjo.2015.09.001
When is macular edema not macular edema? An update on macular telangiectasia type 2
Abstract
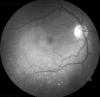
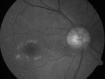
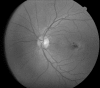
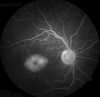
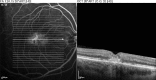
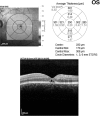
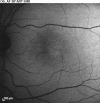
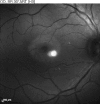
Macular telangiectasia type 2 (Mac Tel 2) also known as idiopathic perifoveal telangiectasia and juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis type 2A is an enigmatic disease of unknown etiology. It manifests both neurodegenerative and vasculopathic characteristics. It manifests itself during the fifth or sixth decades of life. Clinical characteristics include minimally dilated parafoveal capillaries with loss of the retinal transparency in the area involved, absence of lipid exudation, right-angled retinal venules, superficial retinal refractile deposits, hyperplasia of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), foveal atrophy and subretinal neovascularization (SRNV). Optical coherence tomography (OCT) images typically demonstrate outer retinal abnormalities and the presence of intra-retinal hyporeflective spaces that are usually not related with retinal thickening or fluorescein leakage. The typical fluorescein angiographic finding is a deep intraretinal hyperfluorescent staining in the temporal parafoveal area. With time this fluorescein hyperfluorescence involves the whole parafoveal area but does not extend to the center of the fovea. Long-term prognosis for central vision is poor, because of the development of SRNV or macular atrophy. Its pathogenesis remains unclear but multi-modality imaging with fluorescein angiography, spectral domain OCT, adaptive optics, confocal blue reflectance, short wave fundus autofluorescence, OCT angiography, and clinicopathological correlations implicate Müller cells. Currently there is no known treatment for this condition.
Keywords: Müller cells; juxtafoveal retinal telangiectasia; macular telangiectasia; parafoveal telangiectasis; perifoveal telangiectasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: Dr Wu has received lecture fees from Bayer Health and Quantel Medical.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Idiopathic macular telangiectasia type 2 (idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis type 2A, Mac Tel 2).Surv Ophthalmol. 2013 Nov-Dec;58(6):536-59. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2012.11.007. Surv Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 24160729 Review.
-
Multimodality imaging in macular telangiectasia 2: A clue to its pathogenesis.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2015 May;63(5):394-8. doi: 10.4103/0301-4738.159864. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 26139799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnosis of subretinal neovascularization associated with idiopathic juxtafoveal retinal telangiectasia - fluorescein angiography versus spectral-domain optical coherence tomography.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014 Apr;252(4):549-53. doi: 10.1007/s00417-013-2491-4. Epub 2013 Oct 23. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24150706
-
Optical coherence tomography angiography of macular telangiectasia type 1: Comparison with mild diabetic macular edema.Lasers Surg Med. 2017 Mar;49(3):225-232. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22645. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Lasers Surg Med. 2017. PMID: 28168812
-
[Morphological characteristics in macular telangiectasia type 2].Ophthalmologe. 2014 Sep;111(9):819-28. doi: 10.1007/s00347-014-3082-4. Ophthalmologe. 2014. PMID: 25204527 German.
Cited by
-
Choose the right treatment for the right patients.Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2015 Oct-Dec;5(4):147-148. doi: 10.1016/j.tjo.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 29018689 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Unraveling the mysteries of macular telangiectasia 2: the intersection of philanthropy, multimodal imaging and molecular genetics. The 2022 founders lecture of the pan American vitreoretinal society.Int J Retina Vitreous. 2023 Nov 15;9(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s40942-023-00505-5. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2023. PMID: 37968753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Diagnostic Imaging in Macular Telangiectasia Type 2.Fed Pract. 2021 Dec;38(12):594-597. doi: 10.12788/fp.0200. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Fed Pract. 2021. PMID: 35177889 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: internal limiting membrane drape sign masking by foveal detachment in macular telangiectasia type 2.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 Jun 3;20(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12886-020-01485-y. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32493257 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of anatomical and visual outcomes following different anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatments in subretinal neovascular membrane secondary to type 2 proliferative macular telangiectasia.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020 Jan;258(1):99-106. doi: 10.1007/s00417-019-04520-x. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31768680
References
-
- Wu L, Evans T, Arevalo JF. Idiopathic macular telangiectasia type 2 (idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis type 2A, Mac Tel 2) Surv Ophthalmol. 2013;58:536–559. - PubMed
-
- Gass JD, Oyakawa RT. Idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982;100:769–780. - PubMed
-
- Gass JD, Blodi BA. Idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Update of classification and follow-up study. Ophthalmology. 1993;100:1536–1546. - PubMed
-
- Lee ST, Friedman SM, Rubin ML. Cystoid macular edema secondary to juxta-foveolar telangiectasis in Coats’ disease. Ophthalmic Surg. 1991;22:218–221. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

