Visual performance after excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy for high myopia
- PMID: 29018762
- PMCID: PMC5602153
- DOI: 10.4103/tjo.tjo_6_17
Visual performance after excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy for high myopia
Abstract
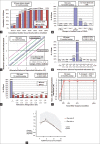
Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy, safety, predictability, and visual performance of excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) for myopia greater than -8 diopters (D).
Methods: Fifty-four patients (104 eyes) with myopia from -8D to -13D and cylinder up to -4D received surface ablation technique with the Allegretto wave version 1009-1 excimer laser to correct their refractive error. The patients were examined on days 1, 3, 7, and 14 and 1, 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively. Visual acuity, manifest refraction, corneal haze, topography, intraocular pressure, contrast sensitivity, and wavefront aberration were evaluated.
Results: Twelve months postoperatively, 95% of eyes were within 1D of the intended correction. In addition, 94% of eyes had attained uncorrected distance visual acuity of 20/25 or better, and 98% of eyes had improved or remained their corrected distance visual acuity. All eyes exhibited barely detectable corneal haze which peaked during the 1st month with a gradual reduction in the 3rd month. Ninety-five percent of patients had no or only mild degree of night glare.
Conclusions: Excimer laser PRK is an effective and predictive treatment for high myopia greater than -8D with or without astigmatism up to -4D. The incidence of complication is low. All patients who are candidates for laser in situ keratomileusis can be candidates for surface ablation, especially those with preoperative thinner cornea or higher risk of corneal flap complications.
Keywords: Excimer laser; myopia; photorefractive keratectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no any conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Trattler WB, Barnes SD. Current trends in advanced surface ablation. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008;19:330–4. - PubMed
-
- Netto MV, Wilson SE. Indications for excimer laser surface ablation. J Refract Surg. 2005;21:734–41. - PubMed
-
- Ghadhfan F, Al-Rajhi A, Wagoner MD. Laser in situ keratomileusis versus surface ablation: Visual outcomes and complications. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33:2041–8. - PubMed
-
- Koller T, Mrochen M, Seiler T. Complication and failure rates after corneal crosslinking. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;35:1358–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

