Susceptibility of different mouse strains to oxaliplatin peripheral neurotoxicity: Phenotypic and genotypic insights
- PMID: 29020118
- PMCID: PMC5636145
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186250
Susceptibility of different mouse strains to oxaliplatin peripheral neurotoxicity: Phenotypic and genotypic insights
Abstract
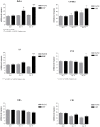
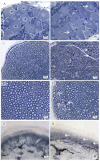
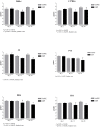
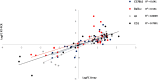
Peripheral neurotoxicity is one of the most distressing side effects of oxaliplatin therapy for cancer. Indeed, most patients that received oxaliplatin experience acute and/or chronic severe sensory peripheral neuropathy. However, despite similar co-morbidities, cancer stage, demographics and treatment schedule, patients develop oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity with remarkably different severity. This suggests individual genetic variability, which might be used to glean the mechanistic insights into oxaliplatin neurotoxicity. We characterized the susceptibility of different mice strains to oxaliplatin neurotoxicity investigating the phenotypic features of neuropathy and gene expression profiles in dorsal root ganglia of six genetically different mice strains (Balb-c, C57BL6, DBA/2J, AJ, FVB and CD1) exposed to the same oxaliplatin schedule. Differential gene expression in dorsal root ganglia from each mice strain were assayed using a genome-wide expression analysis and selected genes were validated by RT-PCR analysis. The demonstration of consistent differences in the phenotypic response to oxaliplatin across different strains is interesting to allow the selection of the appropriate strain based on the pre-defined read-out parameters. Further investigation of the correlation between gene expression changes and oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity phenotype in each strain will be useful to deeper investigate the molecular mechanisms of oxaliplatin neurotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Renn CL, Carozzi VA, Rhee P, Gallop D, Dorsey SG, Cavaletti G. Multimodal assessment of painful peripheral neuropathy induced by chronic oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in mice. Mol Pain. 2011;7:29 doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-29 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Argyriou AA, Bruna J, Marmiroli P, Cavaletti G. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity (CIPN): an update. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2012;82(1):51–77. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2011.04.012 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Staff NP, Grisold A, Grisold W, Windebank AJ. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A current review. Ann Neurol. 2017;81(6):772–81. Epub 2017/06/05. doi: 10.1002/ana.24951 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Atiyyat N, Obaid A. Management of peripheral neuropathy induced by chemotherapy in adults with cancer: a review. Int J Palliat Nurs. 2017;23(1):13–7. doi: 10.12968/ijpn.2017.23.1.13 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Argyriou AA, Bruna J, Genazzani AA, Cavaletti G. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: management informed by pharmacogenetics. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13(8):492–504. Epub 2017/06/30. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2017.88 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

