Time to Sputum Culture Conversion and Treatment Outcomes Among Patients with Isoniazid-Resistant Tuberculosis in Atlanta, Georgia
- PMID: 29020173
- PMCID: PMC5850645
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cix686
Time to Sputum Culture Conversion and Treatment Outcomes Among Patients with Isoniazid-Resistant Tuberculosis in Atlanta, Georgia
Abstract
Background: Although isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis is more common than multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, it has been much less studied. We examined the impact of isoniazid resistance and treatment regimen, including use of a fluoroquinolone, on clinical outcomes.
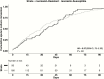
Methods: A retrospective cohort study among patients with sputum culture-positive tuberculosis was performed. Early fluoroquinolone (FQ) use was defined as receiving ≥5 doses during the first month of treatment. The primary outcome was time to sputum culture conversion (tSCC). A multivariate proportional hazards model was used to determine the association of isoniazid resistance with tSCC.
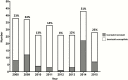
Results: Among 236 patients with pulmonary tuberculosis, 59 (25%) had isoniazid resistance. The median tSCC was similar for isoniazid-resistant and -susceptible cases (35 vs 29 days; P = .39), and isoniazid resistance was not associated with tSCC in multivariate analysis (adjusted hazard ratio = 0.83; 95% confidence interval [CI], .59-1.17). Early FQ use was higher in isoniazid-resistant than -susceptible cases (20% vs 10%; P = .05); however, it was not significantly associated with tSCC in univariate analysis (hazard ratio = 1.48; 95% CI, .95-2.28). Patients with isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis were treated with regimens containing rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol +/- a FQ for a median of 9.7 months. Overall, 191 (83%) patients were cured. There was no difference in initial treatment outcomes; however, all cases of acquired-drug resistance (n = 1) and recurrence (n = 3) occurred among patients with isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis.
Conclusions: There was no significant association with isoniazid resistance and tSCC or initial treatment outcomes. Although patients with isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis had a high cure rate, the cases of recurrence and acquired drug resistance are concerning and highlight the need for longer-term follow-up studies.
Keywords: fluoroquinolones; isoniazid resistance; time to sputum culture conversion; tuberculosis.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Isoniazid Monoresistance and Rate of Culture Conversion among Patients in the State of Georgia with Confirmed Tuberculosis, 2009-2014.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018 Mar;15(3):331-340. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201702-147OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018. PMID: 29131662 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrazinamide may improve fluoroquinolone-based treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Nov;56(11):5465-75. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01300-12. Epub 2012 Aug 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22869570 Free PMC article.
-
Bedaquiline-pretomanid-moxifloxacin-pyrazinamide for drug-sensitive and drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis treatment: a phase 2c, open-label, multicentre, partially randomised controlled trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2024 Sep;24(9):1003-1014. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00223-8. Epub 2024 May 17. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38768617 Clinical Trial.
-
[Effectiveness and problems of PZA-containing 6-month regimen for the treatment of new pulmonary tuberculosis patients].Kekkaku. 2001 Jan;76(1):33-43. Kekkaku. 2001. PMID: 11211781 Review. Japanese.
-
Principles of chemotherapy for tuberculosis in national tuberculosis programmes of low- and middle-income countries.Indian J Tuberc. 2020 Dec;67(4S):S16-S22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijtb.2020.11.010. Epub 2020 Nov 28. Indian J Tuberc. 2020. PMID: 33308663 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment Complexities Among Patients with Tuberculosis in a High HIV Prevalence Cohort in the United States.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2018 Dec;34(12):1050-1057. doi: 10.1089/AID.2018.0126. Epub 2018 Sep 11. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2018. PMID: 30105915 Free PMC article.
-
Increasing Number and Volume of Cavitary Lesions on Chest Computed Tomography Are Associated With Prolonged Time to Culture Conversion in Pulmonary Tuberculosis.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019 Jun 24;6(6):ofz232. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofz232. eCollection 2019 Jun. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31263730 Free PMC article.
-
A 10-year review of isoniazid-resistant TB management in Uzbekistan 2009-2020.IJTLD Open. 2024 Jul 1;1(7):285-291. doi: 10.5588/ijtldopen.23.0533. eCollection 2024 Jul. IJTLD Open. 2024. PMID: 39035427 Free PMC article.
-
Isoniazid Monoresistance and Rate of Culture Conversion among Patients in the State of Georgia with Confirmed Tuberculosis, 2009-2014.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018 Mar;15(3):331-340. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201702-147OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018. PMID: 29131662 Free PMC article.
-
15-year trends in efficacy and effectiveness of treatment outcomes in drug-resistant pulmonary TB.IJTLD Open. 2025 Apr 9;2(4):187-198. doi: 10.5588/ijtldopen.24.0620. eCollection 2025 Apr. IJTLD Open. 2025. PMID: 40226134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2014. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2014.
-
- Gegia M, Winters N, Benedetti A, van Soolingen D, Menzies D. Treatment of isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis with first-line drugs: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2017; 17:223–34. - PubMed
-
- Blumberg HM, Burman WJ, Chaisson RE et al. ; American Thoracic Society, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the Infectious Diseases Society of America American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Infectious Diseases Society of America: treatment of tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003; 167:603–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

