Improvement in Diagnosis of Histoplasma Meningitis by Combined Testing for Histoplasma Antigen and Immunoglobulin G and Immunoglobulin M Anti-Histoplasma Antibody in Cerebrospinal Fluid
- PMID: 29020213
- PMCID: PMC5850023
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cix706
Improvement in Diagnosis of Histoplasma Meningitis by Combined Testing for Histoplasma Antigen and Immunoglobulin G and Immunoglobulin M Anti-Histoplasma Antibody in Cerebrospinal Fluid
Abstract
Background: Central nervous system (CNS) histoplasmosis is a life-threatening condition and represents a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Isolation of Histoplasma capsulatum from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or brain tissue is diagnostic; however, culture is insensitive and slow growth may result in significant treatment delay. We performed a retrospective multicenter study to evaluate the sensitivity and specificity of a new anti-Histoplasma antibody enzyme immunoassay (EIA) for the detection of IgG and IgM antibody in the CSF for diagnosis of CNS histoplasmosis, the primary objective of the study. The secondary objective was to determine the effect of improvements in the Histoplasma galactomannan antigen detection EIA on the diagnosis of Histoplasma meningitis.
Methods: Residual CSF specimens from patients with Histoplasma meningitis and controls were tested for Histoplasma antigen and anti-Histoplasma immunoglobulin G (IgG) and immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibody using assays developed at MiraVista Diagnostics.
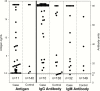
Results: A total of 50 cases and 157 controls were evaluated. Fifty percent of patients with CNS histoplasmosis were immunocompromised, 14% had other medical conditions, and 36% were healthy. Histoplasma antigen was detected in CSF in 78% of cases and the specificity was 97%. Anti-Histoplasma IgG or IgM antibody was detected in 82% of cases and the specificity was 93%. The sensitivity of detection of antibody by currently available serologic testing including immunodiffusion and complement fixation was 51% and the specificity was 96%. Testing for both CSF antigen and antibody by EIA was the most sensitive approach, detecting 98% of cases.
Conclusions: Testing CSF for anti-Histoplasma IgG and IgM antibody complements antigen detection and improves the sensitivity for diagnosis of Histoplasma meningitis.
Keywords: antibody; antigen; diagnosis; histoplasmosis; meningitis.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Wheat LJ, Batteiger BE, Sathapatayavongs B. Histoplasma capsulatum infections of the central nervous system. A clinical review. Medicine (Baltimore) 1990; 69:244–60. - PubMed
-
- Schestatsky P, Chedid MF, Amaral OB, Unis G, Oliveira FM, Severo LC. Isolated central nervous system histoplasmosis in immunocompetent hosts: a series of 11 cases. Scand J Infect Dis 2006; 38:43–8. - PubMed
-
- Gelfand JA, Bennett JE. Active Histoplasma meningitis of 22 years’ duration. JAMA 1975; 233:1294–5. - PubMed
-
- Wheat LJ, Freifeld AG, Kleiman MB et al. . Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical practice guidelines for the management of patients with histoplasmosis: 2007 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 45:807–25. - PubMed
-
- Wheat LJ, Kohler RB, Tewari RP, Garten M, French ML. Significance of Histoplasma antigen in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with meningitis. Arch Intern Med 1989; 149:302–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

