Rapid Detection of Powassan Virus in a Patient With Encephalitis by Metagenomic Sequencing
- PMID: 29020227
- PMCID: PMC5850433
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cix792
Rapid Detection of Powassan Virus in a Patient With Encephalitis by Metagenomic Sequencing
Abstract
We describe a patient with severe and progressive encephalitis of unknown etiology. We performed rapid metagenomic sequencing from cerebrospinal fluid and identified Powassan virus, an emerging tick-borne flavivirus that has been increasingly detected in the United States.
Figures
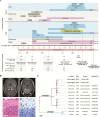
Similar articles
-
Tick-Borne Flaviviruses, with a Focus on Powassan Virus.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2018 Dec 12;32(1):e00106-17. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00106-17. Print 2019 Jan. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 30541872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tick-borne encephalitis virus - a rare cause of encephalitis in infants.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008;120(21-22):710-1. doi: 10.1007/s00508-008-1069-3. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2008. PMID: 19116713 No abstract available.
-
Fatal Powassan Encephalitis (Deer Tick Virus, Lineage II) in a Patient With Fever and Orchitis Receiving Rituximab.JAMA Neurol. 2018 Jun 1;75(6):746-750. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.0132. JAMA Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29554185 Free PMC article.
-
Powassan Virus in a Hunter Returning from a Trip in the Adirondack Park.Wilderness Environ Med. 2020 Mar;31(1):87-90. doi: 10.1016/j.wem.2019.09.002. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Wilderness Environ Med. 2020. PMID: 32007325
-
Laboratory Testing for Powassan Virus: Past, Present, and Future.J Infect Dis. 2024 Aug 14;230(Supplement_1):S70-S75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae197. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39140722 Review.
Cited by
-
Tick-Borne Flaviviruses, with a Focus on Powassan Virus.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2018 Dec 12;32(1):e00106-17. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00106-17. Print 2019 Jan. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 30541872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suspected Neuro-invasive Powassan Virus Infection in a Pediatric Patient.Clin Med Res. 2020 Aug;18(2-3):95-98. doi: 10.3121/cmr.2020.1512. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Clin Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32060042 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogeographic reconstruction of the emergence and spread of Powassan virus in the northeastern United States.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Apr 18;120(16):e2218012120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2218012120. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37040418 Free PMC article.
-
The Brief Case: An unexpected cause of meningoencephalitis in an infant.J Clin Microbiol. 2023 Nov 21;61(11):e0185622. doi: 10.1128/jcm.01856-22. Epub 2023 Nov 21. J Clin Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37987733 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Diagnostic Approach for Arboviral Infections in the United States.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Nov 18;58(12):e01926-19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01926-19. Print 2020 Nov 18. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32938736 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ebel GD, Spielman A, Telford SR 3rd. Phylogeny of North American Powassan virus. J Gen Virol 2001; 82:1657–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

