Detection of Germline Mutations in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Using Multi-gene Panels: Beyond BRCA1/2
- PMID: 29020732
- PMCID: PMC6056949
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2017.220
Detection of Germline Mutations in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Using Multi-gene Panels: Beyond BRCA1/2
Abstract
Purpose: Next-generation sequencing (NGS) allows simultaneous sequencing of multiple cancer susceptibility genes and may represent a more efficient and less expensive approach than sequential testing. We assessed the frequency of germline mutations in individuals with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), using multi-gene panels and NGS.
Materials and methods: Patients with EOC (n=117) with/without a family history of breast or ovarian cancer were recruited consecutively, from March 2016 toDecember 2016.GermlineDNAwas sequenced using 35-gene NGS panel, in order to identify mutations. Upon the detection of a genetic alteration using the panel, results were cross-validated using direct sequencing.
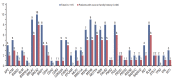
Results: Thirty-eight patients (32.5%) had 39 pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations in eight genes, including BRCA1 (n=21), BRCA2 (n=10), BRIP1 (n=1), CHEK2 (n=2), MSH2 (n=1), POLE (n=1), RAD51C (n=2), and RAD51D (n=2). Among 64 patients with a family history of cancer, 27 (42.2%) had 27 pathogenic or likely pathogenic mutations, and six (9.3%) had mutations in genes other than BRCA1/2, such as CHECK2, MSH2, POLE, and RAD51C. Fifty-five patients (47.0%) were identified to carry only variants of uncertain significance.
Conclusion: Using the multi-gene panel test, we found that, of all patients included in our study, 32.5% had germline cancer-predisposing mutations. NGS was confirmed to substantially improve the detection rates of a wide spectrum of mutations in EOC patients compared with those obtained with the BRCA1/2 testing alone.
Keywords: Ethnicity; Germ-line mutation; Next-generation sequencing; Prevalence; Ovarian epithelial cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures


References
-
- van der Kolk DM, de Bock GH, Leegte BK, Schaapveld M, Mourits MJ, de Vries J, et al. Penetrance of breast cancer, ovarian cancer and contralateral breast cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 families: high cancer incidence at older age. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;124:643–51. - PubMed
-
- Brose MS, Rebbeck TR, Calzone KA, Stopfer JE, Nathanson KL, Weber BL. Cancer risk estimates for BRCA1 mutation carriers identified in a risk evaluation program. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94:1365–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

