Dynamic landscape and regulation of RNA editing in mammals
- PMID: 29022589
- PMCID: PMC5723435
- DOI: 10.1038/nature24041
Dynamic landscape and regulation of RNA editing in mammals
Abstract
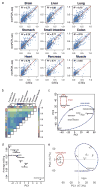
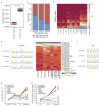
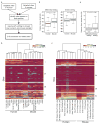
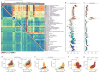
Adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) RNA editing is a conserved post-transcriptional mechanism mediated by ADAR enzymes that diversifies the transcriptome by altering selected nucleotides in RNA molecules. Although many editing sites have recently been discovered, the extent to which most sites are edited and how the editing is regulated in different biological contexts are not fully understood. Here we report dynamic spatiotemporal patterns and new regulators of RNA editing, discovered through an extensive profiling of A-to-I RNA editing in 8,551 human samples (representing 53 body sites from 552 individuals) from the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project and in hundreds of other primate and mouse samples. We show that editing levels in non-repetitive coding regions vary more between tissues than editing levels in repetitive regions. Globally, ADAR1 is the primary editor of repetitive sites and ADAR2 is the primary editor of non-repetitive coding sites, whereas the catalytically inactive ADAR3 predominantly acts as an inhibitor of editing. Cross-species analysis of RNA editing in several tissues revealed that species, rather than tissue type, is the primary determinant of editing levels, suggesting stronger cis-directed regulation of RNA editing for most sites, although the small set of conserved coding sites is under stronger trans-regulation. In addition, we curated an extensive set of ADAR1 and ADAR2 targets and showed that many editing sites display distinct tissue-specific regulation by the ADAR enzymes in vivo. Further analysis of the GTEx data revealed several potential regulators of editing, such as AIMP2, which reduces editing in muscles by enhancing the degradation of the ADAR proteins. Collectively, our work provides insights into the complex cis- and trans-regulation of A-to-I editing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper. Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations
Figures









Comment in
-
Human genomics: Cracking the regulatory code.Nature. 2017 Oct 11;550(7675):190-191. doi: 10.1038/550190a. Nature. 2017. PMID: 29022577 No abstract available.
-
A more personal view of human-gene regulation.Nature. 2017 Oct 11;550(7675):157. doi: 10.1038/550157a. Nature. 2017. PMID: 29022932 No abstract available.
-
Gene-expression study raises thorny ethical issues.Nature. 2017 Oct 11;550(7675):169-170. doi: 10.1038/550169a. Nature. 2017. PMID: 29022940 No abstract available.
-
Gene expression: Principles of gene regulation across tissues.Nat Rev Genet. 2017 Dec;18(12):701. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.94. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Nat Rev Genet. 2017. PMID: 29109523 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA175058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM040536/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007610/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101782/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101810/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA033684/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007593/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI012520/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK098722/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101822/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_U127584490/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK101064/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM124215/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA006227/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG002371/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101819/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA010815/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U127584490/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH090936/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG036695/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000044/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM102484/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK094641/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG007178/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101820/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101825/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090948/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090941/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG007990/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090937/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000029C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101814/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

