Striatal adenosine A2A receptor neurons control active-period sleep via parvalbumin neurons in external globus pallidus
- PMID: 29022877
- PMCID: PMC5655138
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.29055
Striatal adenosine A2A receptor neurons control active-period sleep via parvalbumin neurons in external globus pallidus
Abstract
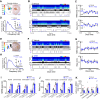
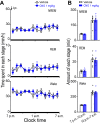
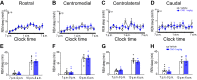
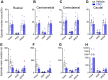
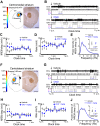
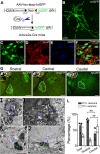
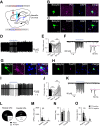
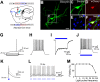
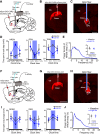
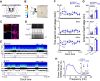
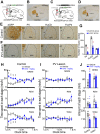
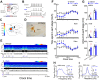
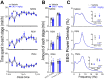
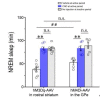
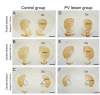
Dysfunction of the striatum is frequently associated with sleep disturbances. However, its role in sleep-wake regulation has been paid little attention even though the striatum densely expresses adenosine A2A receptors (A2ARs), which are essential for adenosine-induced sleep. Here we showed that chemogenetic activation of A2AR neurons in specific subregions of the striatum induced a remarkable increase in non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. Anatomical mapping and immunoelectron microscopy revealed that striatal A2AR neurons innervated the external globus pallidus (GPe) in a topographically organized manner and preferentially formed inhibitory synapses with GPe parvalbumin (PV) neurons. Moreover, lesions of GPe PV neurons abolished the sleep-promoting effect of striatal A2AR neurons. In addition, chemogenetic inhibition of striatal A2AR neurons led to a significant decrease of NREM sleep at active period, but not inactive period of mice. These findings reveal a prominent contribution of striatal A2AR neuron/GPe PV neuron circuit in sleep control.
Keywords: A2A receptor; chemogenetics; mouse; neuroscience; optogenetics; sleep; striatum.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests declared.
Figures

References
-
- Abdi A, Mallet N, Mohamed FY, Sharott A, Dodson PD, Nakamura KC, Suri S, Avery SV, Larvin JT, Garas FN, Garas SN, Vinciati F, Morin S, Bezard E, Baufreton J, Magill PJ. Prototypic and arkypallidal neurons in the dopamine-intact external globus pallidus. Journal of Neuroscience. 2015;35:6667–6688. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4662-14.2015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexander GM, Rogan SC, Abbas AI, Armbruster BN, Pei Y, Allen JA, Nonneman RJ, Hartmann J, Moy SS, Nicolelis MA, McNamara JO, Roth BL. Remote control of neuronal activity in transgenic mice expressing evolved G protein-coupled receptors. Neuron. 2009;63:27–39. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.06.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

