p38α MAPK antagonizing JNK to control the hepatic fat accumulation in pediatric patients onset intestinal failure
- PMID: 29022907
- PMCID: PMC5682685
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2017.523
p38α MAPK antagonizing JNK to control the hepatic fat accumulation in pediatric patients onset intestinal failure
Abstract
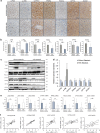
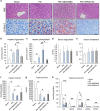
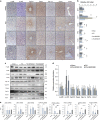
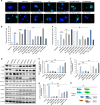
The p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) has been related to gluconeogenesis and lipid metabolism. However, the roles and related mechanisms of p38α MAPK in intestinal failure (IF)-associated liver steatosis remained poor understood. Here, our experimental evidence suggested that p38α MAPK significantly suppressed the fat accumulation in livers of IF patients mainly through two mechanisms. On the one hand, p38α MAPK increased hepatic bile acid (BA) synthesis by upregulating the expression of the rate-limiting enzyme cholesterol 7-α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), which in turn activated the transcription of the CYP7A1. On the other hand, p38α MAPK promoted fatty acid (FA) β-oxidation via upregulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) and its transcriptional target genes carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A (CPT1A) and peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme aoxidase 1 (ACOX1). Dual luciferase assays indicated that p38α MAPK increased the transcription of PPARα, PGC-1α and CYP7A1 by upregulating their promoters' activities. In addition, in vitro and in vivo assays indicated p38α MAPK negatively regulates the hepatic steatosis by controlling JNK activation. In conculsion, our findings demonstrate that hepatic p38α MAPK functions as a negative regulator of liver steatosis in maintaining BA synthesis and FAO by antagonizing the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wiles A, Woodward JM. Recent advances in the management of intestinal failure-associated liver disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2009; 12: 265–272. - PubMed
-
- Carter BA, Karpen SJ. Intestinal failure-associated liver disease: management and treatment strategies past, present, and future. Semin Liver Dis 2007; 27: 251–258. - PubMed
-
- Lauriti G, Zani A, Aufieri R, Cananzi M, Chiesa PL, Eaton S et al. Incidence, prevention, and treatment of parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis and intestinal failure-associated liver disease in infants and children: a systematic review. JPEN 2014; 38: 70–85. - PubMed
-
- Kurvinen A, Nissinen MJ, Andersson S, Korhonen P, Ruuska T, Taimisto M et al. Parenteral plant sterols and intestinal failure-associated liver disease in neonates. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2012; 54: 803–811. - PubMed
-
- Nehra D, Fallon EM, Puder M. The prevention and treatment of intestinal failure-associated liver disease in neonates and children. Surg Clin N Am 2011; 91: 543–563. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

