Reproducible diagnosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia by flow cytometry: An European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC) & European Society for Clinical Cell Analysis (ESCCA) Harmonisation project
- PMID: 29024461
- PMCID: PMC5817234
- DOI: 10.1002/cyto.b.21595
Reproducible diagnosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia by flow cytometry: An European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC) & European Society for Clinical Cell Analysis (ESCCA) Harmonisation project
Abstract
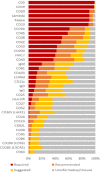
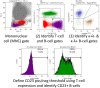
The diagnostic criteria for CLL rely on morphology and immunophenotype. Current approaches have limitations affecting reproducibility and there is no consensus on the role of new markers. The aim of this project was to identify reproducible criteria and consensus on markers recommended for the diagnosis of CLL. ERIC/ESCCA members classified 14 of 35 potential markers as "required" or "recommended" for CLL diagnosis, consensus being defined as >75% and >50% agreement, respectively. An approach to validate "required" markers using normal peripheral blood was developed. Responses were received from 150 participants with a diagnostic workload >20 CLL cases per week in 23/150 (15%), 5-20 in 82/150 (55%), and <5 cases per week in 45/150 (30%). The consensus for "required" diagnostic markers included: CD19, CD5, CD20, CD23, Kappa, and Lambda. "Recommended" markers potentially useful for differential diagnosis were: CD43, CD79b, CD81, CD200, CD10, and ROR1. Reproducible criteria for component reagents were assessed retrospectively in 14,643 cases from 13 different centers and showed >97% concordance with current approaches. A pilot study to validate staining quality was completed in 11 centers. Markers considered as "required" for the diagnosis of CLL by the participants in this study (CD19, CD5, CD20, CD23, Kappa, and Lambda) are consistent with current diagnostic criteria and practice. Importantly, a reproducible approach to validate and apply these markers in individual laboratories has been identified. Finally, a consensus "recommended" panel of markers to refine diagnosis in borderline cases (CD43, CD79b, CD81, CD200, CD10, and ROR1) has been defined and will be prospectively evaluated. © 2017 International Clinical Cytometry Society.
Keywords: chronic lymphocytic leukemia; diagnosis; flow cytometry.
© 2017 The Authors. Cytometry Part B: Clinical Cytometry published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of International Clinical Cytometry Society.
Figures
References
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J, Vardiman JW. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. WHO Press, 2008.
-
- Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, Caligaris‐Cappio F, Dighiero G, Döhner H, Hillmen P, Keating MJ, Montserrat E, Rai KR, Kipps TJ. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a report from the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute‐Working Group 1996 guidelines. Blood 2008;111:5446–5456. - PMC - PubMed
-
- NCCN ‐ Evidence‐Based Cancer Guidelines, Oncology Drug Compendium, Oncology Continuing Medical Education. https://www.nccn.org/ (accessed 3 Sep 2016).
-
- Puente XS, Beà S, Valdés‐Mas R, Villamor N, Gutiérrez‐Abril J, Martín‐Subero JI, Munar M, Rubio‐Pérez C, Jares P, Aymerich M, Baumann T, Beekman R, Belver L, Carrio A, Castellano G, Clot G, Colado E, Colomer D, Costa D, Delgado J, Enjuanes A, Estivill X, Ferrando AA, Gelpí JL, González B, González S, González M, Gut M, Hernández‐Rivas JM, López‐Guerra M, Martín‐García D, Navarro A, Nicolás P, Orozco M, Payer ÁR, Pinyol M, Pisano DG, Puente DA, Queirós AC, Quesada V, Romeo‐Casabona CM, Royo C, Royo R, Rozman M, Russiñol N, Salaverría I, Stamatopoulos K, Stunnenberg HG, Tamborero D, Terol MJ, Valencia A, López‐Bigas N, Torrents D, Gut I, López‐Guillermo A, López‐Otín C, Campo E. Non‐coding recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2015;526:519–524. - PubMed
-
- Matutes E, Owusu‐Ankomah K, Morilla R, Garcia Marco J, Houlihan A, Que TH, Catovsky D. The immunological profile of B‐cell disorders and proposal of a scoring system for the diagnosis of CLL. Leukemia 1994;8 :1640–1645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

