High validity of cardiomyopathy diagnoses in western Sweden (1989-2009)
- PMID: 29024504
- PMCID: PMC5880670
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.12224
High validity of cardiomyopathy diagnoses in western Sweden (1989-2009)
Abstract
Aim: Hospital discharges with a diagnosis of cardiomyopathy have more than doubled in Sweden since 1987. We validated the cardiomyopathy diagnoses over this time period to investigate that the increase was real and not a result of improved recognition of the diagnosis and better diagnostic methods.
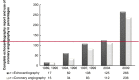
Methods and results: Every fifth year from 1989 to 2009, records for all patients with a cardiomyopathy diagnosis were identified by searching the local registers in three hospitals in Västra Götaland, Sweden. The diagnoses were validated according to criteria defined by the European Society of Cardiology from 2008. The population comprised 611 cases with cardiomyopathy diagnoses [mean age 58.9 (SD 15.5) years, 68.2% male], divided into three major groups: dilated, hypertrophic, and other cardiomyopathies. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy were analysed as a group. Cardiomyopathies for which there were few cases, such as restrictive, arrhythmogenic right ventricular, left ventricular non-compaction, takotsubo, and peripartum cardiomyopathies, were analysed together and defined as 'other cardiomyopathies'. Relevant co-morbidities were registered. The use of echocardiography was 99.7%, of which 94.6% was complete echocardiography reports. The accuracy rates of the diagnoses dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and other cardiomyopathies were 85.5%, 87.5%, and 100%, respectively, with no differences between the three hospitals or years studied; nor did the prevalence of co-morbidities differ.
Conclusions: The accuracy rate of the cardiomyopathy diagnoses from in-hospital records from >600 patients in western Sweden during a 20 year period was 86.6%, with no significant trend over time, strengthening epidemiological findings that this is likely due to an actual increase in cardiomyopathy diagnoses rather than changes in coding practices. The use of echocardiography was high, and there was no significant difference in co-morbidities during the study period. The accuracy rate of the cardiomyopathy diagnoses during the 20 year period was high. The use of diagnostic tools did not increase under the study period, and once cardiomyopathy diagnoses were suspected, echocardiography was performed in almost all cases. In this study, the occurrence of cardiomyopathy was increasing over time without significant increase of co-morbidity, supporting that an actual increase of cardiomyopathy has occurred.
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy; Co-morbidity; Diagnosis; Validation.
© 2017 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
References
-
- Kannel WB. Incidence and epidemiology of heart failure. Heart Fail Rev 2000; 5: 167–173. - PubMed
-
- Ponikowski P. 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 2016; 37: 2129–2200. - PubMed
-
- McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, Auricchio A, Böhm M, Dickstein K, Falk V, Filippatos G, Fonseca C, Gomez‐Sanchez MA, Jaarsma T, Køber L, Lip GY, Maggioni AP, Parkhomenko A, Pieske BM, Popescu BA, Rønnevik PK, Rutten FH, Schwitter J, Seferovic P, Stepinska J, Trindade PT, Voors AA, Zannad F, Zeiher A; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines . ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2012; 33: 1787–1847. - PubMed
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JG, Coats AJ, Falk V, González‐Juanatey JR, Harjola VP, Jankowska EA, Jessup M, Linde C, Nihoyannopoulos P, Parissis JT, Pieske B, Riley JP, Rosano GM, Ruilope LM, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, van der Meer P; Authors/Task Force Members . 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2016; 37: 2129–2200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical