Dynamics of Gut-Brain Communication Underlying Hunger
- PMID: 29024666
- PMCID: PMC5691364
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.09.043
Dynamics of Gut-Brain Communication Underlying Hunger
Abstract
Communication between the gut and brain is critical for homeostasis, but how this communication is represented in the dynamics of feeding circuits is unknown. Here we describe nutritional regulation of key neurons that control hunger in vivo. We show that intragastric nutrient infusion rapidly and durably inhibits hunger-promoting AgRP neurons in awake, behaving mice. This inhibition is proportional to the number of calories infused but surprisingly independent of macronutrient identity or nutritional state. We show that three gastrointestinal signals-serotonin, CCK, and PYY-are necessary or sufficient for these effects. In contrast, the hormone leptin has no acute effect on dynamics of these circuits or their sensory regulation but instead induces a slow modulation that develops over hours and is required for inhibition of feeding. These findings reveal how layers of visceral signals operating on distinct timescales converge on hypothalamic feeding circuits to generate a central representation of energy balance.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

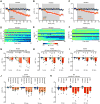
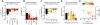

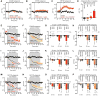

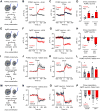

Similar articles
-
Gut-to-brain signals in feeding control.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Feb 1;320(2):E326-E332. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00388.2020. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33284086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Identification of Vagal Sensory Neurons That Control Feeding.Cell. 2019 Nov 14;179(5):1129-1143.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.031. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31730854 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of pups suppresses hunger-induced feeding in virgin adult mice of both sexes.Neuroscience. 2017 Oct 24;362:228-238. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.08.047. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 28882425
-
The gut and energy balance: visceral allies in the obesity wars.Science. 2005 Mar 25;307(5717):1909-14. doi: 10.1126/science.1109951. Science. 2005. PMID: 15790843 Review.
-
Nutritive, Post-ingestive Signals Are the Primary Regulators of AgRP Neuron Activity.Cell Rep. 2017 Dec 5;21(10):2724-2736. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.11.036. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 29212021 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Network dynamics of hypothalamic feeding neurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Apr 6;118(14):e2011140118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2011140118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33795520 Free PMC article.
-
Food-induced dopamine signaling in AgRP neurons promotes feeding.Cell Rep. 2022 Nov 29;41(9):111718. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111718. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36450244 Free PMC article.
-
Paraventricular Thalamic MC3R Circuits Link Energy Homeostasis with Anxiety-Related Behavior.J Neurosci. 2023 Sep 6;43(36):6280-6296. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0704-23.2023. Epub 2023 Aug 17. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37591737 Free PMC article.
-
Carnitine acetyltransferase (Crat) in hunger-sensing AgRP neurons permits adaptation to calorie restriction.FASEB J. 2018 Jun 22;32(12):fj201800634R. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800634R. Online ahead of print. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29932868 Free PMC article.
-
POMC neurons in heat: A link between warm temperatures and appetite suppression.PLoS Biol. 2018 May 7;16(5):e2006188. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2006188. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Biol. 2018. PMID: 29734335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becskei C, Lutz TA, Riediger T. Glucose reverses fasting-induced activation in the arcuate nucleus of mice. Neuroreport. 2008;19:105–109. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

