A conceptual framework for evaluating data suitability for observational studies
- PMID: 29024976
- PMCID: PMC7378879
- DOI: 10.1093/jamia/ocx095
A conceptual framework for evaluating data suitability for observational studies
Abstract
Objective: To contribute a conceptual framework for evaluating data suitability to satisfy the research needs of observational studies.
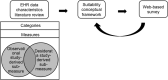
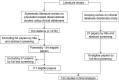
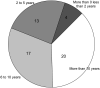
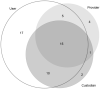
Materials and methods: Suitability considerations were derived from a systematic literature review on researchers' common data needs in observational studies and a scoping review on frequent clinical database design considerations, and were harmonized to construct a suitability conceptual framework using a bottom-up approach. The relationships among the suitability categories are explored from the perspective of 4 facets of data: intrinsic, contextual, representational, and accessible. A web-based national survey of domain experts was conducted to validate the framework.
Results: Data suitability for observational studies hinges on the following key categories: Explicitness of Policy and Data Governance, Relevance, Availability of Descriptive Metadata and Provenance Documentation, Usability, and Quality. We describe 16 measures and 33 sub-measures. The survey uncovered the relevance of all categories, with a 5-point Likert importance score of 3.9 ± 1.0 for Explicitness of Policy and Data Governance, 4.1 ± 1.0 for Relevance, 3.9 ± 0.9 for Availability of Descriptive Metadata and Provenance Documentation, 4.2 ± 1.0 for Usability, and 4.0 ± 0.9 for Quality.
Conclusions: The suitability framework evaluates a clinical data source's fitness for research use. Its construction reflects both researchers' points of view and data custodians' design features. The feedback from domain experts rated Usability, Relevance, and Quality categories as the most important considerations.
Keywords: data suitability; observational studies; survey.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Medical Informatics Association. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Blumenthal D,Tavenner M. The “meaningful use” regulation for electronic health records.N Engl J Med. 2010;363:501–04. - PubMed
-
- Schubart JR,Einbinder JS. Evaluation of a data warehouse in an academic health sciences center.Int J Med Inf. 2000;60:319–33. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

