Impact of adding hand-washing and water disinfection promotion to oral cholera vaccination on diarrhoea-associated hospitalization in Dhaka, Bangladesh: evidence from a cluster randomized control trial
- PMID: 29025064
- PMCID: PMC5837384
- DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyx187
Impact of adding hand-washing and water disinfection promotion to oral cholera vaccination on diarrhoea-associated hospitalization in Dhaka, Bangladesh: evidence from a cluster randomized control trial
Abstract
Background: Information on the impact of hygiene interventions on severe outcomes is limited. As a pre-specified secondary outcome of a cluster-randomized controlled trial among >400 000 low-income residents in Dhaka, Bangladesh, we examined the impact of cholera vaccination plus a behaviour change intervention on diarrhoea-associated hospitalization.
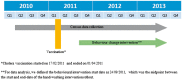
Methods: Ninety neighbourhood clusters were randomly allocated into three areas: cholera-vaccine-only; vaccine-plus-behaviour-change (promotion of hand-washing with soap plus drinking water chlorination); and control. Study follow-up continued for 2 years after intervention began. We calculated cluster-adjusted diarrhoea-associated hospitalization rates using data we collected from nearby hospitals, and 6-monthly census data of all trial households.
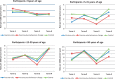
Results: A total of 429 995 people contributed 500 700 person-years of data (average follow-up 1.13 years). Vaccine coverage was 58% at the start of analysis but continued to drop due to population migration. In the vaccine-plus-behaviour-change area, water plus soap was present at 45% of hand-washing stations; 4% of households had detectable chlorine in stored drinking water. Hospitalization rates were similar across the study areas [events/1000 person-years, 95% confidence interval (CI), cholera-vaccine-only: 9.4 (95% CI: 8.3-10.6); vaccine-plus-behaviour-change: 9.6 (95% CI: 8.3-11.1); control: 9.7 (95% CI: 8.3-11.6)]. Cholera cases accounted for 7% of total number of diarrhoea-associated hospitalizations.
Conclusions: Neither cholera vaccination alone nor cholera vaccination combined with behaviour-change intervention efforts measurably reduced diarrhoea-associated hospitalization in this highly mobile population, during a time when cholera accounted for a small fraction of diarrhoea episodes. Affordable community-level interventions that prevent infection from multiple pathogens by reliably separating faeces from the environment, food and water, with minimal behavioural demands on impoverished communities, remain an important area for research.
Keywords: Vaccine; diarrhoea; hand-washing; hospitalization; water treatment.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Epidemiological Association
Figures

References
-
- Liu L, Oza S, Hogan D. et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2000–13, with projections to inform post-2015 priorities: an updated systematic analysis. Lancet 2015;385:430–40. - PubMed
-
- Black RE, Cousens S, Johnson HL. et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2008: a systematic analysis. Lancet 2010;375:1969–87. - PubMed
-
- National Institute of Population Research and Training (NIPORT), Mitra and Associates, and ICF International. Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey 2014: Key Indicators. Dhaka, Bangladesh, and Rockville, MD: NIPORT, Mitra and Associates, and ICF International, 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

