Using the capture-recapture method to estimate the human immunodeficiency virus-positive population
- PMID: 29025259
- PMCID: PMC5675981
- DOI: 10.4178/epih.e2017042
Using the capture-recapture method to estimate the human immunodeficiency virus-positive population
Abstract
Objectives: The capture-recapture method was applied to estimate the number of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-positive individuals not registered with any data sources.
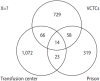
Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted in Lorestan Province, in the west of Iran, in 2016. Three incomplete sources of HIV-positive individuals, with partially overlapping data, were used, including: (a) transfusion center, (b) volunteer counseling and testing centers (VCTCs), and (c) prison. The 3-source capture-recapture method, using a log-linear model, was applied for data analysis. The Akaike information criterion and the Bayesian information criterion were used for model selection.
Results: Of the 2,456 HIV-positive patients registered in these 3 data sources, 1,175 (47.8%) were identified in transfusion center, 867 (35.3%) in VCTCs, and 414 (16.8%) in prison. After the exclusion of duplicate entries, 2,281 HIV-positive patients remained. Based on the capture-recapture method, 14,868 (95% confidence interval, 9,923 to 23,427) HIV-positive individuals were not identified in any of the registries. Therefore, the real number of HIV-positive individuals was estimated to be 17,149, and the overall completeness of the 3 registries was estimated to be around 13.3%.
Conclusions: Based on capture-recapture estimates, a huge number of HIV-positive individuals are not registered with any of the provincial data sources. This is an urgent message for policymakers who plan and provide health care services for HIV-positive patients. Although the capture-recapture method is a useful statistical approach for estimating unknown populations, due to the assumptions and limitations of the method, the population size may be overestimated as it seems possible in our results.
Keywords: Capture-recapture method; HIV seropositivity; Iran; Linear models.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare for this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estimation of the Frequency of Intravenous Drug Users in Hamadan City, Iran, Using the Capture-recapture Method.Epidemiol Health. 2012;34:e2012006. doi: 10.4178/epih/e2012006. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Epidemiol Health. 2012. PMID: 23173080 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian estimation of a cancer population by capture-recapture with individual capture heterogeneity and small sample.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2015 Apr 24;15:39. doi: 10.1186/s12874-015-0029-7. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2015. PMID: 25902941 Free PMC article.
-
[HIV-positive drug users in South Limburg: number and characteristics, a capture-recapture analysis].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2001 Jun 9;145(23):1118-22. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2001. PMID: 11450606 Dutch.
-
The applications of capture-recapture models to epidemiological data.Stat Med. 2001 Oct 30;20(20):3123-57. doi: 10.1002/sim.996. Stat Med. 2001. PMID: 11590637 Review.
-
[Capture-recapture method--an instrument for estimating TB prevalence].Pneumologia. 2006 Oct-Dec;55(4):167-70. Pneumologia. 2006. PMID: 17494271 Review. Romanian.
Cited by
-
On some pitfalls of the log-linear modeling framework for capture-recapture studies in disease surveillance.Epidemiol Methods. 2023 Jan;12(Suppl 1):20230019. doi: 10.1515/em-2023-0019. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Epidemiol Methods. 2023. PMID: 39829734 Free PMC article.
-
Using Capture-Recapture Methodology to Enhance Precision of Representative Sampling-Based Case Count Estimates.J Surv Stat Methodol. 2022 Jan 5;10(5):1292-1318. doi: 10.1093/jssam/smab052. eCollection 2022 Nov. J Surv Stat Methodol. 2022. PMID: 36397765 Free PMC article.
-
Tailoring capture-recapture methods to estimate registry-based case counts based on error-prone diagnostic signals.Stat Med. 2023 Jul 30;42(17):2928-2943. doi: 10.1002/sim.9759. Epub 2023 May 9. Stat Med. 2023. PMID: 37158167 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating the number of farms experienced foot and mouth disease outbreaks using capture-recapture methods.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2020 Nov 19;53(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s11250-020-02452-x. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2020. PMID: 33211202
-
A capture-recapture modeling framework emphasizing expert opinion in disease surveillance.Stat Methods Med Res. 2024 Jul;33(7):1197-1210. doi: 10.1177/09622802241254217. Epub 2024 May 20. Stat Methods Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38767225 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Guidelines on estimating the size of populations most at risk to HIV. 2010 [cited 2017 Oct 18]. Available from: http://data.unaids.org/pub/manual/2010/guidelines_popnestimationsize_en.pdf.
-
- Bernard HR, Johnsen EC, Killworth PD, Robinson S. Estimating the size of an average personal network and of an event subpopulation: some empirical results. Soc Sci Res. 1991;20:109–121.
-
- Clague A. Introductory note on census enumeration. 2001 [cited 2017 Oct 25]. Available from: https://unstats.un.org/unsd/demographic/meetings/egm/symposium2001/docs/....
-
- Chao A, Tsay PK, Lin SH, Shau WY, Chao DY. The applications of capture‐recapture models to epidemiological data. Stat Med. 2001;20:3123–3157. - PubMed
-
- University of Pittsburgh Capture-recapture. 2017 [cited 2017 May 27]. Available from: http://www.pitt.edu/~yuc2/cr/
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources