Ion channels of the lung and their role in disease pathogenesis
- PMID: 29025712
- PMCID: PMC5792182
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00285.2017
Ion channels of the lung and their role in disease pathogenesis
Abstract
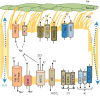
Maintenance of normal epithelial ion and water transport in the lungs includes providing a thin layer of surface liquid that coats the conducting airways. This airway surface liquid is critical for normal lung function in a number of ways but, perhaps most importantly, is required for normal mucociliary clearance and bacterial removal. Preservation of the appropriate level of hydration, pH, and viscosity for the airway surface liquid requires the proper regulation and function of a battery of different types of ion channels and transporters. Here we discuss how alterations in ion channel/transporter function often lead to lung pathologies.
Keywords: chloride channels; oxidants; potasium channels; sodium channels.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Alimohammadi M, Dubois N, Sköldberg F, Hallgren A, Tardivel I, Hedstrand H, Haavik J, Husebye ES, Gustafsson J, Rorsman F, Meloni A, Janson C, Vialettes B, Kajosaari M, Egner W, Sargur R, Pontén F, Amoura Z, Grimfeld A, De Luca F, Betterle C, Perheentupa J, Kämpe O, Carel JC. Pulmonary autoimmunity as a feature of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 and identification of KCNRG as a bronchial autoantigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 4396–4401, 2009. doi:10.1073/pnas.0809986106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anaparti V, Pascoe CD, Jha A, Mahood TH, Ilarraza R, Unruh H, Moqbel R, Halayko AJ. Tumor necrosis factor regulates NMDA receptor-mediated airway smooth muscle contractile function and airway responsiveness. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 311: L467–L480, 2016. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00382.2015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Åstrand AB, Hemmerling M, Root J, Wingren C, Pesic J, Johansson E, Garland AL, Ghosh A, Tarran R. Linking increased airway hydration, ciliary beating, and mucociliary clearance through ENaC inhibition. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 308: L22–L32, 2015. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00163.2014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

