Histone deacetylase inhibitors downregulate CCR4 expression and decrease mogamulizumab efficacy in CCR4-positive mature T-cell lymphomas
- PMID: 29025909
- PMCID: PMC5777200
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2017.177279
Histone deacetylase inhibitors downregulate CCR4 expression and decrease mogamulizumab efficacy in CCR4-positive mature T-cell lymphomas
Abstract
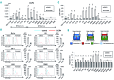
Histone deacetylase inhibitors are promising agents for various T-cell lymphomas, including cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, peripheral T-cell lymphoma, and adult T-cell lymphoma/leukemia. CCR4 is an important therapeutic target molecule because mogamulizumab, an anti-CCR4 antibody, has shown promising efficacy against various T-cell lymphomas. In this study, we examined the in vitro synergistic effects of mogamulizumab and histone deacetylase inhibitors against various T-cell lymphomas. First, we examined the expression of CCR4 mRNA and surface CCR4 in various T-cell lymphoma cell lines and found that it was downregulated upon treatment with vorinostat, a pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor. Next, we used isoform-specific histone deacetylase inhibitors and short-interfering RNA to determine the histone deacetylase isoform involved in the regulation of CCR4, and demonstrated that romidepsin, a class I selective histone deacetylase inhibitor, reduced CCR4 most efficiently. Moreover, among class I histone deacetylases, histone deacetylase 2 knockdown led to a reduction of CCR4 in lymphoma cells, suggesting that CCR4 expression is mainly regulated by histone deacetylase 2. When we examined the CCR4 expression in skin samples from primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, obtained from the same patients before and after vorinostat treatment, we found that CCR4 expression was greatly reduced after treatment. Finally, when we conducted an antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity assay with mogamulizumab by using various lymphoma cells, we found that the efficacy of mogamulizumab was significantly reduced by pretreatment with vorinostat. Altogether, our results suggest that the primary use of histone deacetylase inhibitors before treatment with mogamulizumab might not be suitable to obtain synergistic effects. Moreover, these results have potential implications for optimal therapeutic sequences in various CCR4-positive T-cell lymphomas.
Copyright© 2018 Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures



References
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid tissues 2008. 4th ed. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC).
-
- O’Leary HM, Savage KJ. Update on the World Health Organization classification of peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2009;4(4): 227–235. - PubMed
-
- Savage KJ. Therapies for peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011;2011:515–524. - PubMed
-
- Vose J, Armitage J, Weisenburger D. International peripheral T-cell and natural killer/T-cell lymphoma study: pathology findings and clinical outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(25):4124–4130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

