Low-Level Endogenous PSMA Expression in Nonprostatic Tumor Xenografts Is Sufficient for In Vivo Tumor Targeting and Imaging
- PMID: 29025989
- PMCID: PMC5868500
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.117.191221
Low-Level Endogenous PSMA Expression in Nonprostatic Tumor Xenografts Is Sufficient for In Vivo Tumor Targeting and Imaging
Abstract
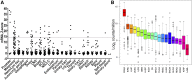
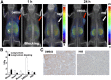
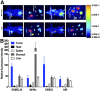
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is highly expressed in prostate cancer and within the neovasculature of other solid tumors. The nonprostatic expression of PSMA has been reported exclusively within the neovasculature endothelial cells of nonprostatic cancers; however, there are few reports on PSMA expression in epithelial cells. Herein, we describe PSMA expression in nonprostatic epithelial cells and characterize the potential of PSMA-binding agents to noninvasively detect that expression. Methods: PSMA expression data were extracted from publicly available genomic databases. Genomic data were experimentally validated for PSMA expression-by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, flow cytometry, and Western blotting-in several nonprostatic cell lines and xenografts of melanoma and small cell lung cancer (SCLC) origin. The feasibility of PSMA detection in those tumor models was further established using PSMA-based nuclear and optical imaging agents and by biodistribution, blocking, and ex vivo molecular characterization studies. Results: We discovered that a small percentage of nonprostatic cancer cell lines and tumors express PSMA. Importantly, PSMA expression was sufficiently high to image established melanoma and SCLC xenografts using PSMA-based nuclear and optical imaging agents. Conclusion: These results indicate that PSMA expression in nonprostatic tumors may not be limited to the endothelium but may also include solid tumor tissue of nonprostatic cancers including melanoma and SCLC. Our observations indicate broader applicability of PSMA-targeted imaging and therapeutics.
Keywords: CCLE; TCGA; lung cancer; melanoma; molecular imaging; prostate cancer.
© 2018 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures


References
-
- Pavlícek J, Ptacek J, Bařinka C. Glutamate carboxypeptidase II: an overview of structural studies and their importance for structure-based drug design and deciphering the reaction mechanism of the enzyme. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19:1300–1309. - PubMed
-
- Sweat SD, Pacelli A, Murphy GP, Bostwick DG. Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression is greatest in prostate adenocarcinoma and lymph node metastases. Urology. 1998;52:637–640. - PubMed
-
- Bostwick DG, Pacelli A, Blute M, Roche P, Murphy GP. Prostate specific membrane antigen expression in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma: a study of 184 cases. Cancer. 1998;82:2256–2261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
