Enhanced antifungal activity of voriconazole-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers against Candida albicans with a dimorphic switching model
- PMID: 29026306
- PMCID: PMC5627732
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S145695
Enhanced antifungal activity of voriconazole-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers against Candida albicans with a dimorphic switching model
Abstract
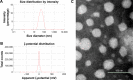
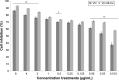
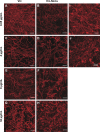
Candida commonly adheres to implanted medical devices and forms biofilms. Due to the minimal activity of current antifungals against biofilms, new drugs or drug-delivery systems to treat these persistent infections are urgently needed. In the present investigation, voriconazole-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (Vrc-NLCs) were formulated for enhanced drug-delivery efficiency to C. albicans to increase the antifungal activity of Vrc and to improve the treatment of infectious Candida diseases. Vrc-NLCs were prepared by a hot-melt, high-pressure homogenization method, and size distribution, ζ-potential, morphology, drug-encapsulation efficiency, drug loading, and physical stability were characterized. The antifungal activity of Vrc-NLCs in vitro was tested during planktonic and biofilm growth in C. albicans. The mean particle size of the Vrc-NLCs was 45.62±0.53 nm, and they exhibited spheroid-like morphology, smooth surfaces, and ζ-potential of -0.69±0.03 mV. Encapsulation efficiency and drug loading of Vrc-NLCs were 75.37%±2.65% and 3.77%±0.13%, respectively. Physical stability results revealed that despite the low measured ζ-potential, the dispersion of the Vrc-NLCs was stable during their 3-week storage at 4°C. The minimum inhibitory concentration of Vrc-NLCs was identical to that of Vrc. However, the inhibition rate of Vrc-NLCs at lower concentrations was significantly higher than that of Vrc during planktonic growth in C. albicans in yeast-extract peptone dextrose medium. Surprisingly, Vrc-NLCs treatment reduced cell density in biofilm growth in C. albicans and induced more switches form hyphal cells to yeast cells compared with Vrc treatment. In conclusion, Vrc-NLCs maintain antifungal activity of Vrc and increase antifungal drug-delivery efficiency to C. albicans. Therefore, Vrc-NLCs will greatly contribute to the treatment of infectious diseases caused by C. albicans.
Keywords: Candida albicans; antifungal activity; biofilms; nanostructured lipid carriers; voriconazole.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antifungal activity of amphotericin B and voriconazole against the biofilms and biofilm-dispersed cells of Candida albicans employing a newly developed in vitro pharmacokinetic model.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2015 Apr 3;14:21. doi: 10.1186/s12941-015-0083-3. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2015. PMID: 25885806 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization, stabilization, and characterization of amphotericin B loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for ocular drug delivery.Int J Pharm. 2019 Dec 15;572:118771. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118771. Epub 2019 Oct 26. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31669555 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular Inserts of Voriconazole-Loaded Proniosomal Gels: Formulation, Evaluation and Microbiological Studies.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Oct 12;15:7825-7840. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S268208. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33116503 Free PMC article.
-
Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLCs) for Drug Delivery: Role of Liquid Lipid (Oil).Curr Drug Deliv. 2021;18(3):249-270. doi: 10.2174/1567201817666200423083807. Curr Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 32324512 Review.
-
Impact of multiscale surface topography characteristics on Candida albicans biofilm formation: From cell repellence to fungicidal activity.Acta Biomater. 2024 Mar 15;177:20-36. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.02.006. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Acta Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38342192 Review.
Cited by
-
Striking Back against Fungal Infections: The Utilization of Nanosystems for Antifungal Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 18;22(18):10104. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810104. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incorporation of Nonyl 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoate Into Nanostructured Lipid Systems: Effective Alternative for Maintaining Anti-Dermatophytic and Antibiofilm Activities and Reducing Toxicity at High Concentrations.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jun 5;11:1154. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01154. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32582096 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and in vivo evaluation of a highly skin- and nail-permeable efinaconazole topical formulation for enhanced treatment of onychomycosis.Drug Deliv. 2019 Dec;26(1):1167-1177. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2019.1687612. Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 31738083 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation Development, Characterization and Antifungal Evaluation of Chitosan NPs for Topical Delivery of Voriconazole In Vitro and Ex Vivo.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Dec 30;14(1):135. doi: 10.3390/polym14010135. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35012154 Free PMC article.
-
Development of antifungal fibrous ocular insert using freeze-drying technique.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Sep;14(9):2520-2538. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01527-8. Epub 2024 Feb 16. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38366116 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

